Question 1:
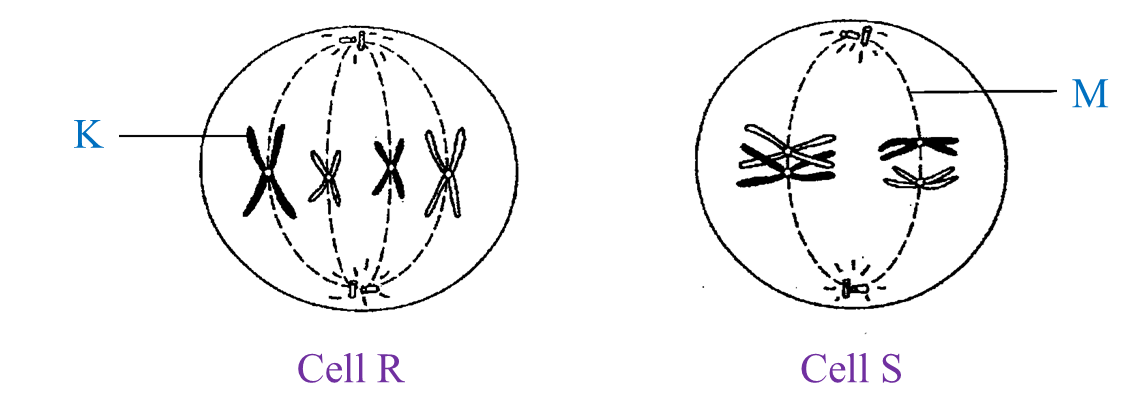
Diagram I shows the different stages in a cell division.
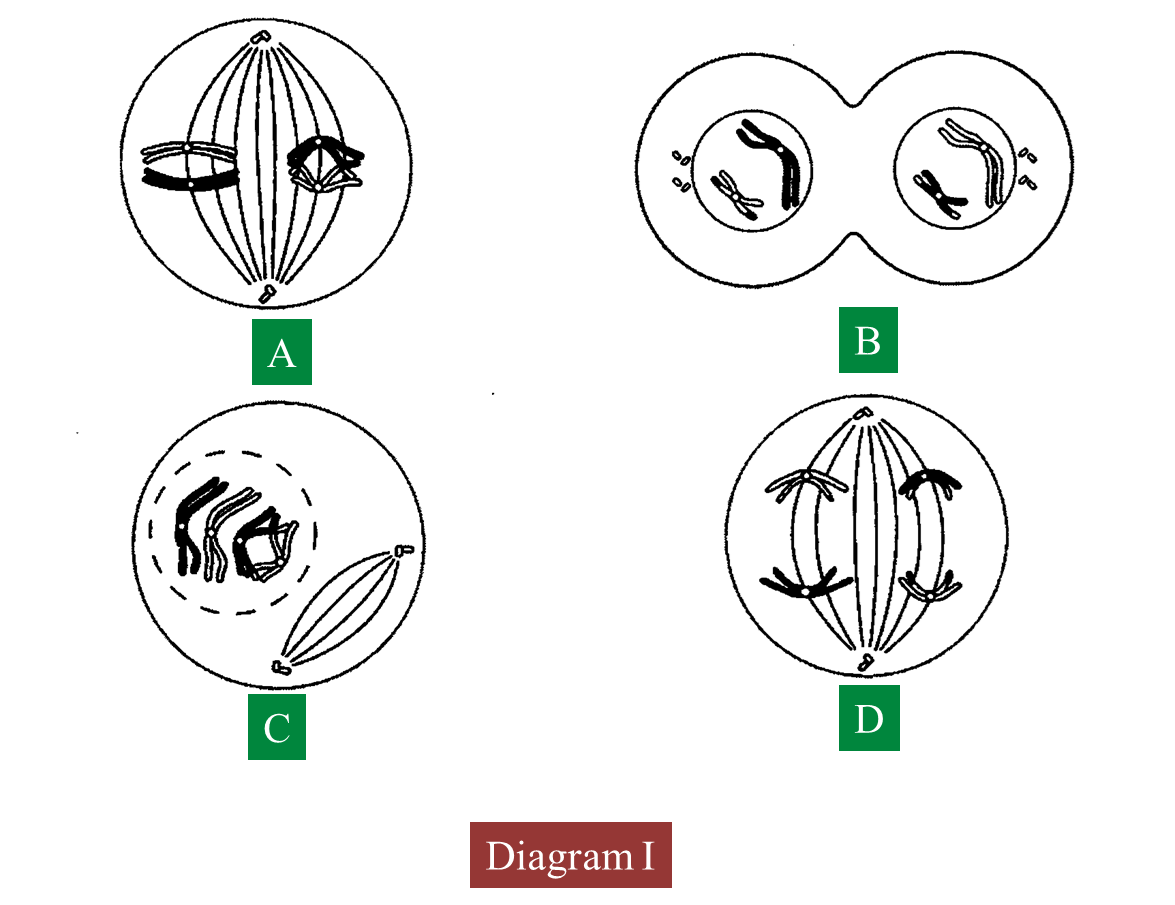
(a)(i) Name the type of cell division.
(a)(ii) Arrange the stages of the cell division in the correct sequence.
(b)(i) Explain the chromosomal behaviour in stage C.
(b)(ii) State one importance of the chromosomal behaviour in (b)(i).
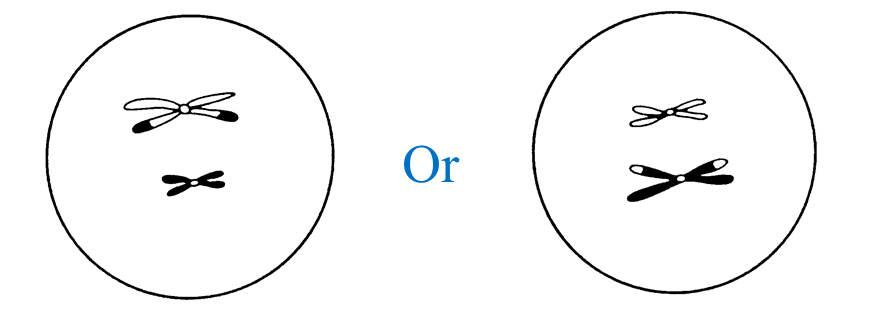
(c) Diagram II shows the involvement of cells produced by this type of cell division in the formation of zygote.
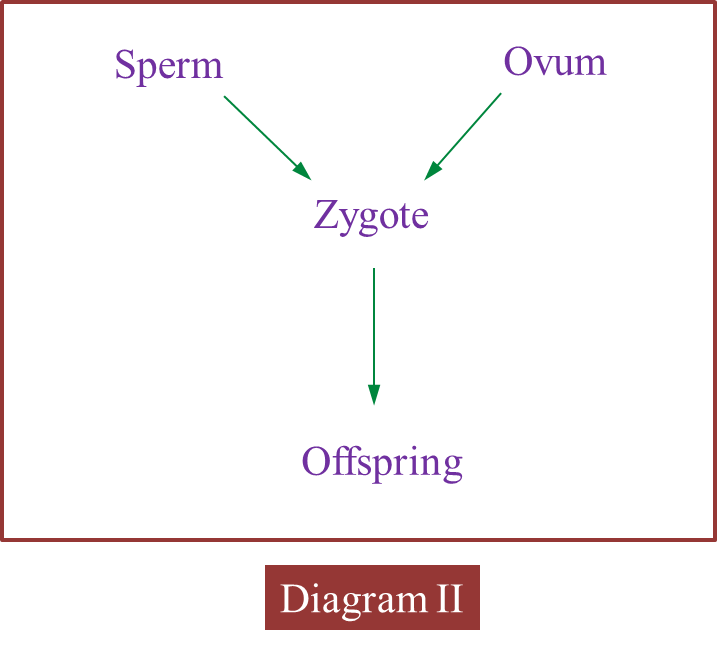
Explain how zygote is formed.
(d) Diagram III shows the karyotype of an offspring produced.
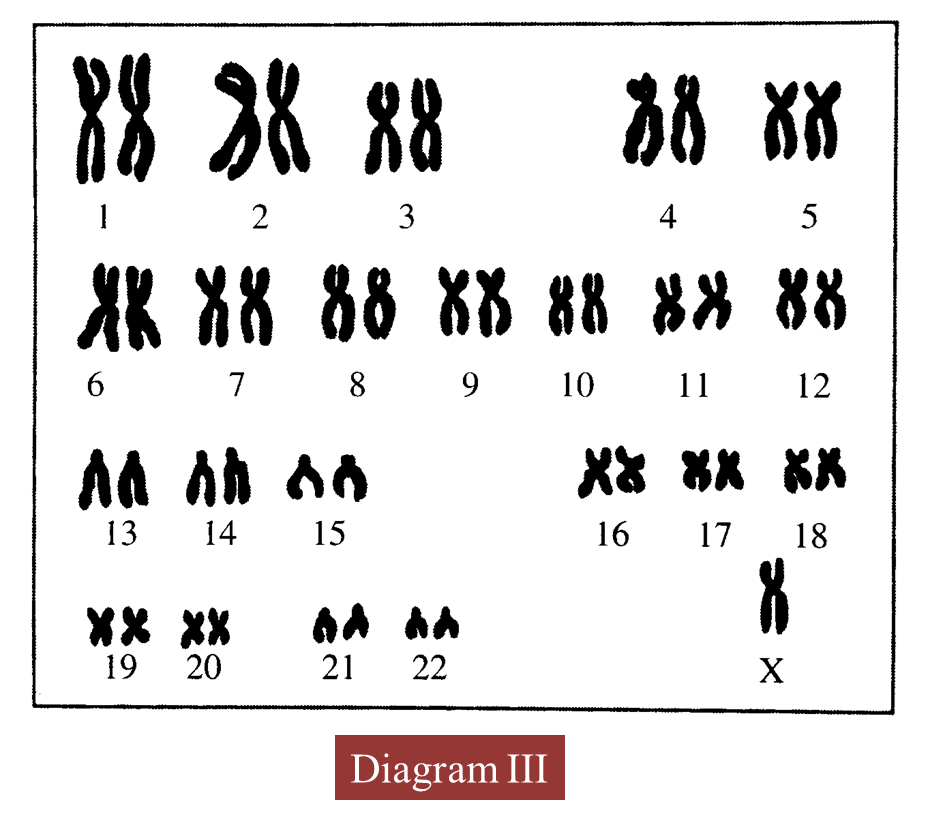
(i) State the number of chromosomes in the offspring.
(ii) Name the genetic disease suffered by the offspring.
(iii) Give one reason for the answer in (d)(ii).
(iv) Explain how radioactive rays can cause this genetic disease.
Answer:
(a)(i)
Meiosis I
(a)(ii)
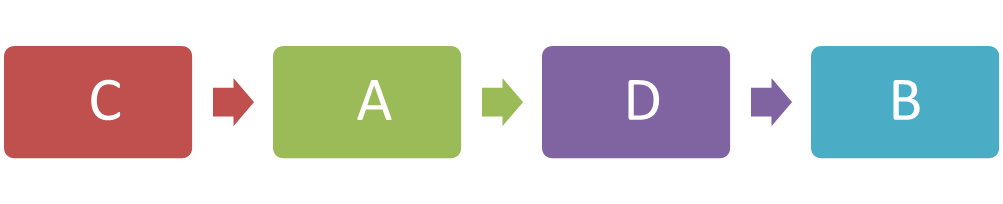
(b)(i)
The chromosomes condense, thicken and become clear.
Homologous chromosome exchange the genetic material in a process of crossing over.
(b)(ii)
Increases genetic diversity/ causes variation.
(c)
When the nucleus of a sperm (haploid) fuses with the nucleus of an ovum (haploid) during fertilization, a zygote (diploid) is formed.
(d)(i)
45/ 44 + X
(d)(ii)
Turner’s syndrome
(d)(iii)
The absence of one X chromosome which is a sex chromosome
(d)(iv)
Radioactive radiation can cause mutation of the chromosomes, as a result of which only one X chromosome is present.
Diagram I shows the different stages in a cell division.

(a)(i) Name the type of cell division.
(a)(ii) Arrange the stages of the cell division in the correct sequence.

(b)(i) Explain the chromosomal behaviour in stage C.
(b)(ii) State one importance of the chromosomal behaviour in (b)(i).
(c) Diagram II shows the involvement of cells produced by this type of cell division in the formation of zygote.

Explain how zygote is formed.
(d) Diagram III shows the karyotype of an offspring produced.

(i) State the number of chromosomes in the offspring.
(ii) Name the genetic disease suffered by the offspring.
(iii) Give one reason for the answer in (d)(ii).
(iv) Explain how radioactive rays can cause this genetic disease.
Answer:
(a)(i)
Meiosis I
(a)(ii)

(b)(i)
The chromosomes condense, thicken and become clear.
Homologous chromosome exchange the genetic material in a process of crossing over.
(b)(ii)
Increases genetic diversity/ causes variation.
(c)
When the nucleus of a sperm (haploid) fuses with the nucleus of an ovum (haploid) during fertilization, a zygote (diploid) is formed.
(d)(i)
45/ 44 + X
(d)(ii)
Turner’s syndrome
(d)(iii)
The absence of one X chromosome which is a sex chromosome
(d)(iv)
Radioactive radiation can cause mutation of the chromosomes, as a result of which only one X chromosome is present.