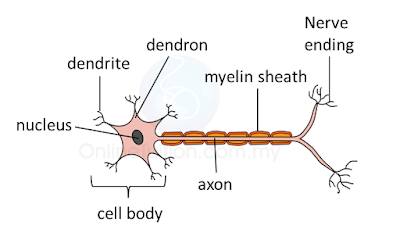
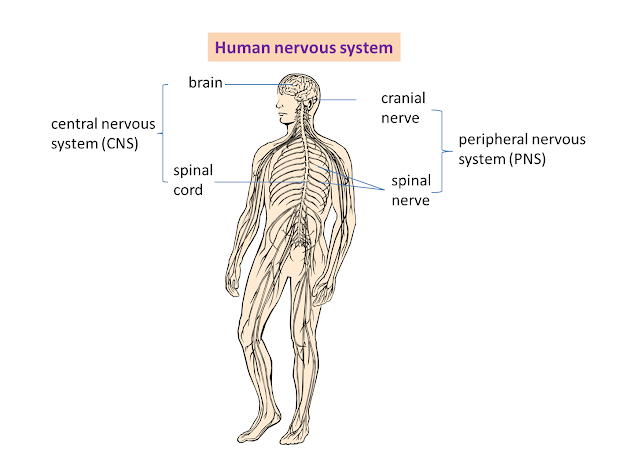
Types of Neurone
There are three types of neurone:
(a) Sensory neurone
(b) Relay neurone (intermediate neurone)
(c) Motor neuroneCharacteristics |
Sensory neurone |
Relay neurone |
Motor neurone |
Position in the body |
Present in all parts of the body |
Present in the brain and the spinal cord only |
Present in all parts of the body |
Position of cell body |
In the middle of neurone |
At the centre of neurone |
At the end of neurone |
Length of axon |
Short |
Very short |
Long |
Function |
Transmits impulses from a receptor to the central nervous system |
Transmits impulses from a sensory neurone to a motor neurone |
Transmits impulses from the central nervous system to the effector |