The Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is a semi-permeable lipid bilayer found in all cells that controls water and certain substances in and out of the cell.Function of the Plasma Membrane
- Protects the cell.
- Separates the intracellular components from the extracellular environment.
- Controls what enters and exits the cell
Necessities for the Movement of Substances across the Plasma Membrane
- To transport nutrients into the cell.
- For gases exchange
- To excrete metabolic waste.
- To maintain the pH value and ionic concentration of the cell.
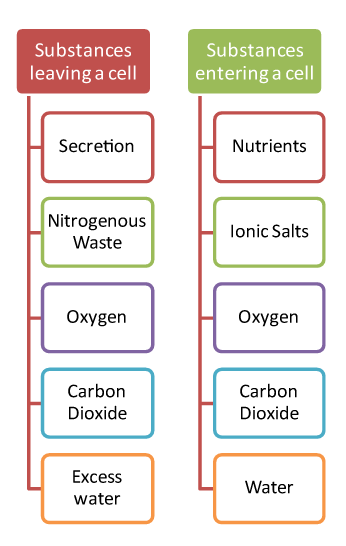
Substances In and Out through the Membrane
Structure of the Plasma Membrane
Fluid Mosaic Model
Internet Resources (Flash Animation)
Permeability of the Phospholipids Bilayer
The permeability of the phospholipids bilayer is determined by:- the size
- the charge and
- the polarity
