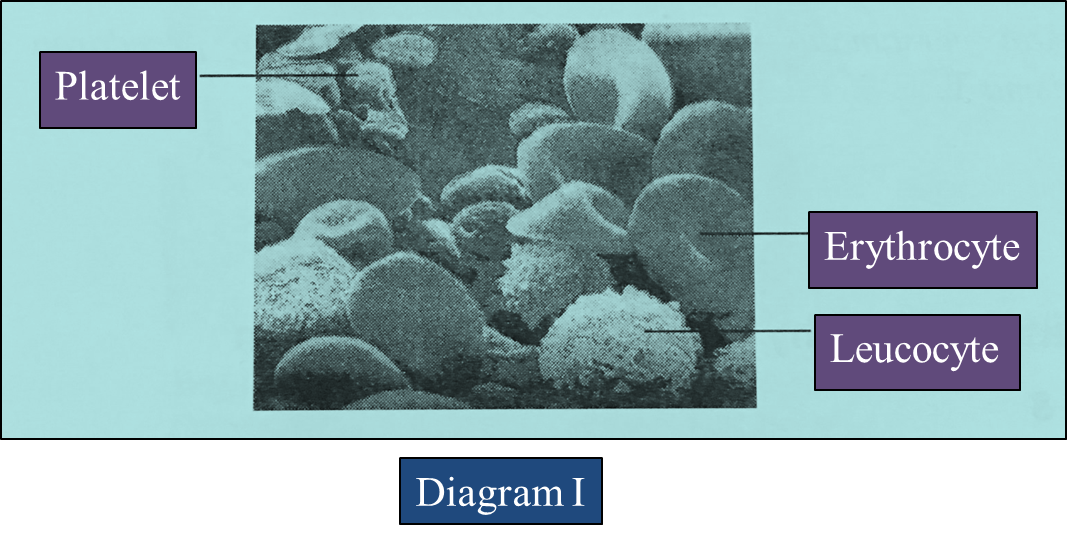
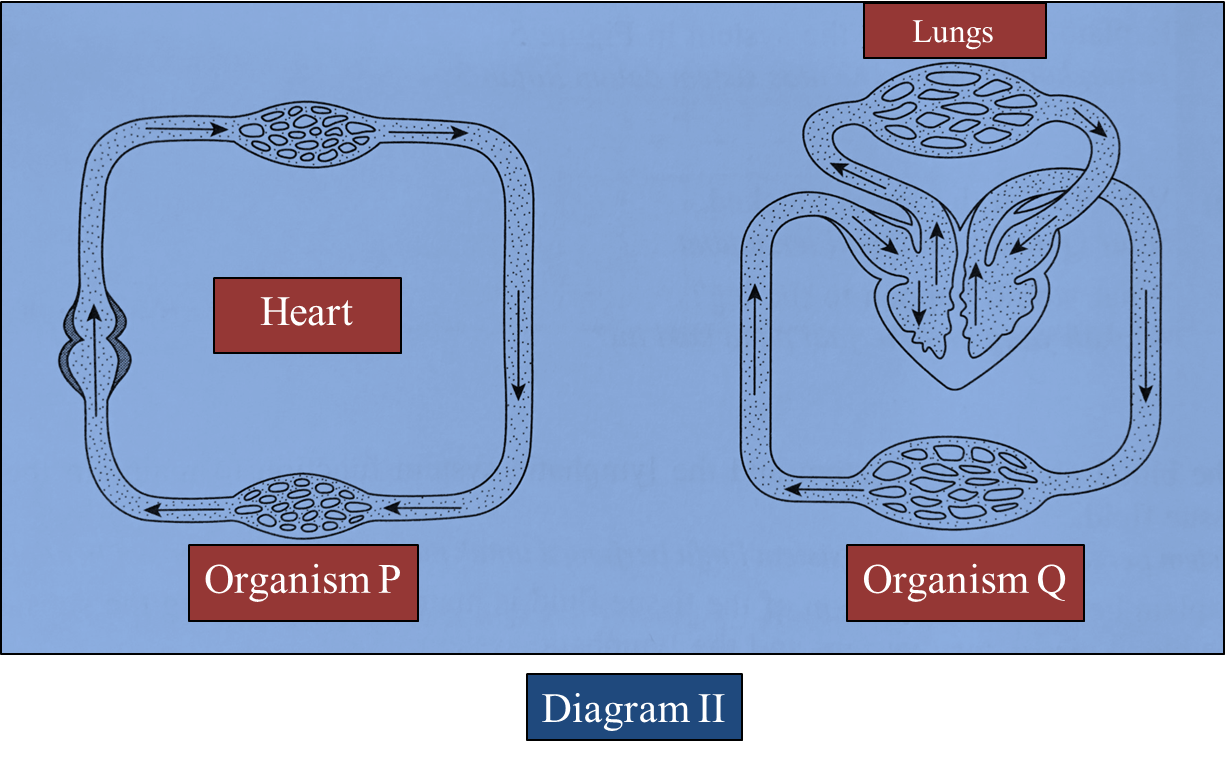
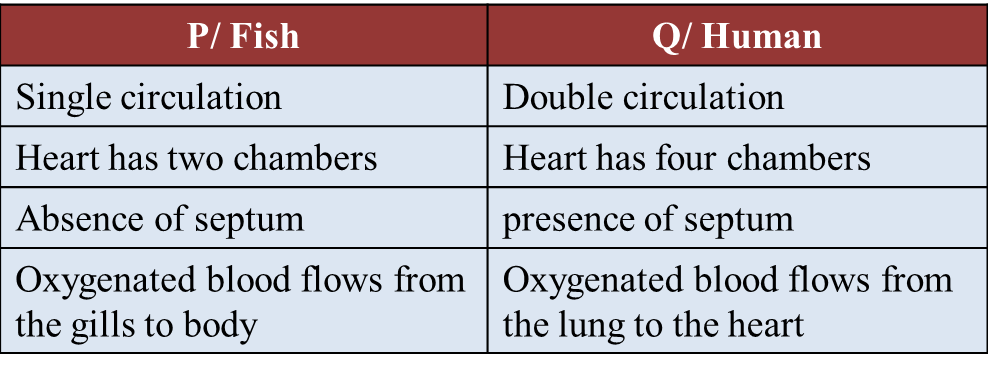
Question 1:
Figure below shows part of the circulatory system and the lymphatic system in the human body.
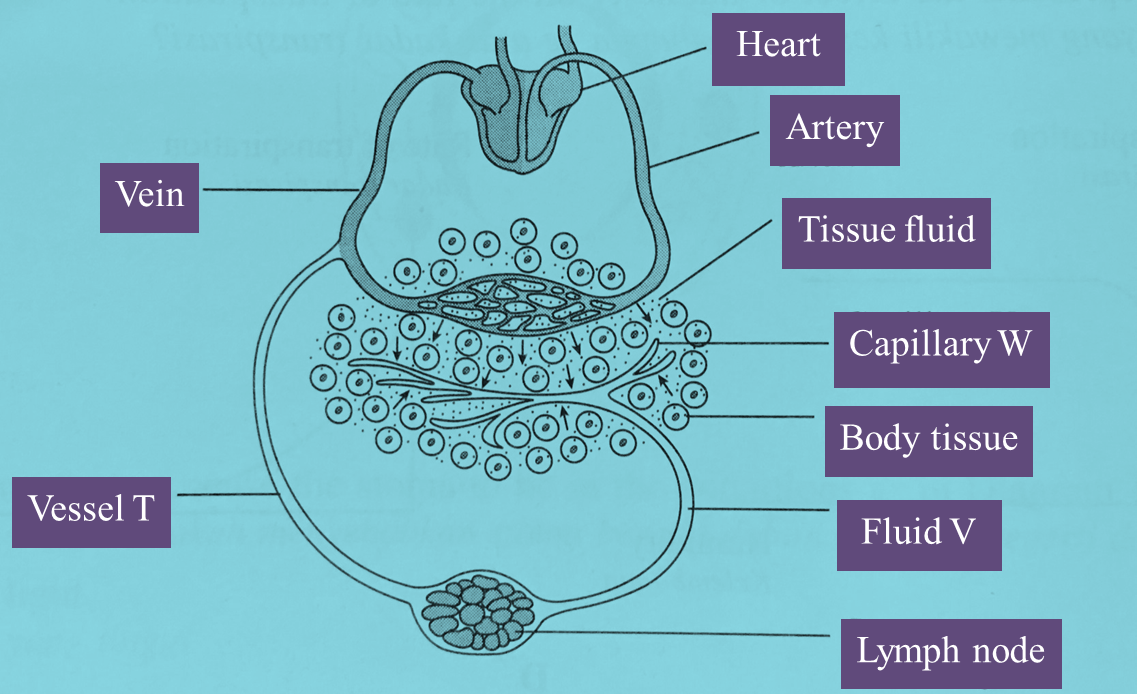
(a)(i) What is fluid V? [1 mark]
(ii) What happens to the components of fluid V when it passes through the lymph node? [1 mark]
(b)(i) Fluid V originates from the blood.
Describe how fluid V is formed from the blood. [2 marks]
(ii) State one difference between fluid V and the blood. [1 mark]
(c)(i) A part of vessel T is blocked.
Explain its effect on the system in the Figure. [2 marks]
(ii) Vessel T in the leg is blocked.
What would happen to the leg? [1 mark]
(d) The blood circulatory system and the lymphatic system function to maintain the composition of the tissue fluid.
Explain how the composition of the tissue fluid is maintained by stating the substances transported by the blood circulatory system and the lymphatic system. [3 marks]
Answer:
(a)(i)
Fluid V = Lymph
(a)(ii)
Toxic substances and pathogens are neutralized/ destroyed.
(b)(i)
Blood plasma diffuses from the capillaries. The tissue fluid formed diffuses into the lymphatic vessels.
(b)(ii)
Fluid V does not have erythrocytes whereas blood has erythrocytes. Fluid V is clear yellowish whereas blood is red in colour.
(c)(i)
Interstitial fluid fails to return to the blood circulatory system. Tissue fluid accumulates in the spaces between the cells.
(c)(ii)
The leg will be swollen.
(d)
Dissolved substances such as glucose and amino acids are transported in the blood circulatory system entering the body tissues forming tissue fluid. Fatty acids and glycerol are transported by the lymphatic system into the blood circulatory system. Some of the contents of the tissue fluid enter the lymphatic system and some enter the blood circulatory system at the ends of the venules.
Figure below shows part of the circulatory system and the lymphatic system in the human body.

(a)(i) What is fluid V? [1 mark]
(ii) What happens to the components of fluid V when it passes through the lymph node? [1 mark]
(b)(i) Fluid V originates from the blood.
Describe how fluid V is formed from the blood. [2 marks]
(ii) State one difference between fluid V and the blood. [1 mark]
(c)(i) A part of vessel T is blocked.
Explain its effect on the system in the Figure. [2 marks]
(ii) Vessel T in the leg is blocked.
What would happen to the leg? [1 mark]
(d) The blood circulatory system and the lymphatic system function to maintain the composition of the tissue fluid.
Explain how the composition of the tissue fluid is maintained by stating the substances transported by the blood circulatory system and the lymphatic system. [3 marks]
Answer:
(a)(i)
Fluid V = Lymph
(a)(ii)
Toxic substances and pathogens are neutralized/ destroyed.
(b)(i)
Blood plasma diffuses from the capillaries. The tissue fluid formed diffuses into the lymphatic vessels.
(b)(ii)
Fluid V does not have erythrocytes whereas blood has erythrocytes. Fluid V is clear yellowish whereas blood is red in colour.
(c)(i)
Interstitial fluid fails to return to the blood circulatory system. Tissue fluid accumulates in the spaces between the cells.
(c)(ii)
The leg will be swollen.
(d)
Dissolved substances such as glucose and amino acids are transported in the blood circulatory system entering the body tissues forming tissue fluid. Fatty acids and glycerol are transported by the lymphatic system into the blood circulatory system. Some of the contents of the tissue fluid enter the lymphatic system and some enter the blood circulatory system at the ends of the venules.