10.1 Circles I
10.1.1 Parts of a Circle
1. A circle is set of points in a plane equidistant from a fixed point.
2. Parts of a circle:
(a) The centre, O, of a circle is a fixed point which is equidistant from all points on the circle.


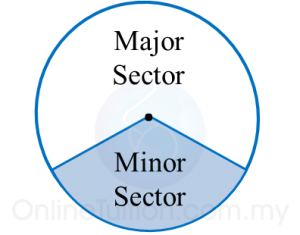
(b) A sector is the region enclosed by two radii and an arc.
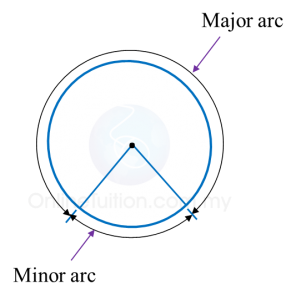
(c) An arc is a part of the circumference of a circle.
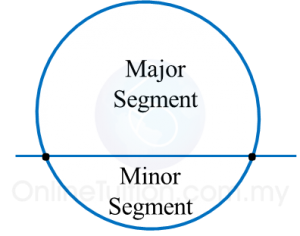
(d) A segment is an area enclosed by an arc and a chord.
10.1.2 Circumference of a Circle
circumference=πd, where d=diameter =2πr, where r=radius π(pi)=227 or 3.142
Example:
Calculate the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 14 cm.
(π=227)
Solution:
10.1.3 Arc of a Circle
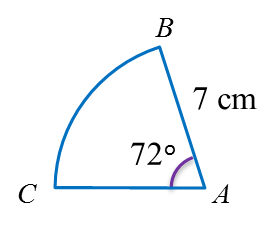
The length of an arc of a circle is proportional to the angle at the centre.
Length of arcCircumference=Angle at centre360o
Example:
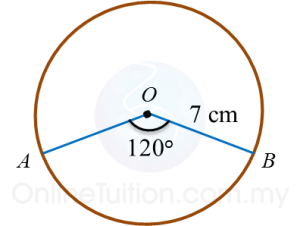
Calculate the length of the minor arc AB of the circle above.
(π=227)
Solution:
Length of arcCircumference=Angle at centre360oLength of arcAB=120o360o×2×227×7=1423cm
10.1.4 Area of a Circle
Area of a circle = π×(radius)2 =πr2
Example:
Calculate the area of each of the following circles that has
(a) a radius of 7 cm,
(b) a diameter of 10 cm.
(π=227)
Solution:
(a)
Area of a circle=πr2=227×7×7=154cm2
(b)
Diameter of circle=10cmRadius of circle=5cmArea of circle=πr2=227×5×5=78.57cm2