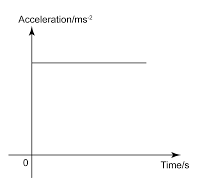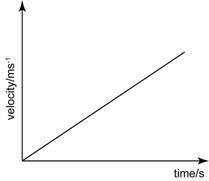
- The gradient of the velocity-time gradient gives a value of the changing rate in velocity, which is the acceleration of the object.
- The area below the velocity-time graph gives a value of the object's displacement.
Analysing Velocity-Time Graph
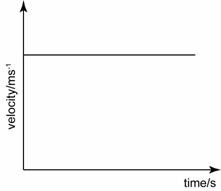
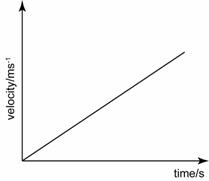
- When analysing velocity-time graph, always keep in mind that the gradient of the graph is equal to the acceleration of the graph.
- If the gradient is constant, then the acceleration is constant. If the gradient increase, then the acceleration increase and etc.
- Table below shows a few cases of velocity-time graph for different types of motion.
Uniform velocity
Uniform acceleration
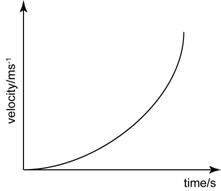
Increasing acceleration
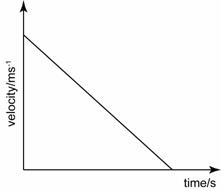
Uniform deceleration
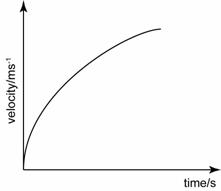
Decreasing acceleration
Converting a Velocity-Time graph to Acceleration-Time graph
- In order to convert a velocity-time graph to acceleration time graph, we need to find the gradient of the velocity time graph and plot it in the acceleration-time graph.
- The 5th and 6th videos below explain how to sketch an acceleration-time graph form a given velocity-time graph.
Free Falling
- Free falling is a motion under gravitational force as the only force acting on the moving object.
- The acceleration of a free falling object is always constant.
- On the surface of the earth, the acceleration of is equal to 10ms-2, and is named as gravitational acceleration.
- In SPM, you need to know the graphs of free falling of the following movement
- Launching object upward.
- Dropping Object from High Place
- Object Falling and Bounce Back
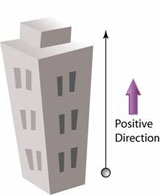
Launching Object Upward
- When you launch an object upward, its velocity decreases at a constant rate, hence it's a straight line with negative gradient in a velocity-time graph.
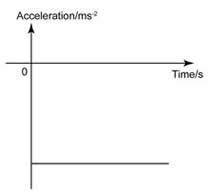
- Since the velocity decreases at a constant rate, hence the acceleration is constant. Also, the acceleration is negative because the speed decreases in positive direction. Therefore, the acceleration graph is a horizontal line in the negative domain.
Motion
\
Velocity-Time Graph
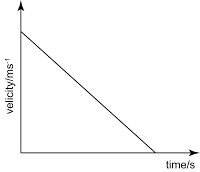
Acceleration-Time Graph
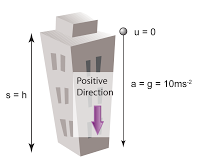
Dropping Object from a High Place
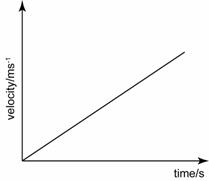
- When an object drops from a high place, its velocity increases at a constant rate, hence it's a straight line with positive gradient in a velocity-time graph.
- Since the velocity increases at a constant rate and the speed increases in positive direction hence the acceleration is constant and positive.
Motion

Velocity-Time Graph
Acceleration-Time Graph
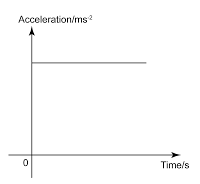
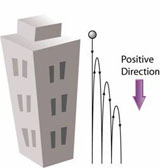
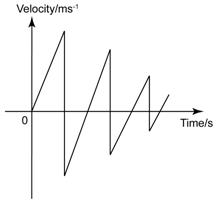
Object Falling and Bounce Back
Motion
Velocity-Time Graph
.png)
Acceleration-Time Graph