- Two objects are in thermal contact when heat energy can be transferred between them.
- Two objects are in thermal equilibrium when there is no net flow of heat between two objects that are in thermal equilibrium.
- Two objects in thermal equilibrium have the same temperature.
Example:
Figure below shows 2 blocks in thermal contact with each other. Initially, the temperature of the 2 blocks are different, and there is a net flow of thermal energy from higher temperature to lower temperature.
After some time, thermal equilibrium achieved, where the temperature of the 2 blocks become the same, and there is no net flow of thermal energy between the 2 blocks.
Before
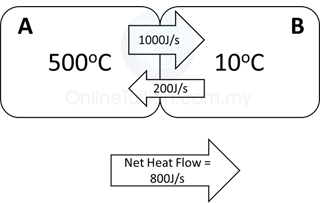
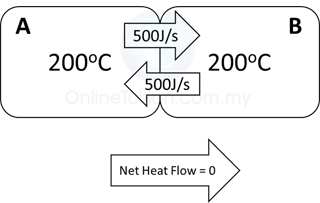
Figure below shows 2 blocks in thermal contact with each other. Initially, the temperature of the 2 blocks are different, and there is a net flow of thermal energy from higher temperature to lower temperature.
After some time, thermal equilibrium achieved, where the temperature of the 2 blocks become the same, and there is no net flow of thermal energy between the 2 blocks.
Before

- Initially, the temperature of block A is higher than block B.
- The rate of thermal energy transfer is higher from block A to the block B (1000J/s).
- There is also thermal energy transfer from the block B to block A, but with lower rate (only at 200J/s).
- Therefore, there is a net heat flow of thermal energy from the block A to block B.
- As a result, the temperature of block A decreases whereas the temperature of B increases.

- Thermal Equilibrium Achieved.
- The temperature of the 2 blocks become the same.
- Heat flow is still goes on between the blocks.
- However, the rate of flow of heat are equal in both direction. As a result, the net heat flow is equal to 0.
Objective Question:
2 iron blocks, P and Q are in thermal contact. The initial temperature of P and Q are 10°C and 50°C respectively. Which of the followings is true when P and Q are at thermal equilibrium.
Answer:
The correct answer is II and III.
Answer I. is incorrect.
When 2 objects achieve thermal equilibrium, the temperature of the 2 objects will be the same.
Answer II. is correct.
When 2 objects achieve thermal equilibrium, the rate of flow of heat is equal, hence there is no net flow of heat between the 2 objects.
Answer III. is correct.
When P and Q are in thermal contact, the temperature of P (10°C)will increase whereas the temperature of Q (50°C) will decrease. When P and Q are in thermal equilibrium the temperature of P and Q will be the same and the temperature will be higher than 10°C but lower than 50°C.
Answer IV. is incorrect.
In thermal equilibrium, there is still heat flow between P and Q.
However, the rate of the heat flow is equal in both direction (P to Q and Q to P), hence the net flow of heat between P and Q is zero.
2 iron blocks, P and Q are in thermal contact. The initial temperature of P and Q are 10°C and 50°C respectively. Which of the followings is true when P and Q are at thermal equilibrium.
- The temperature of P will be higher than the temperature of Q.
- The net flow of heat between P and Q is zero
- The temperature of P and Q will be lower than 50°C but higher than 10°C.
- There is no heat flow between the 2 blocks.
Answer:
The correct answer is II and III.
Answer I. is incorrect.
When 2 objects achieve thermal equilibrium, the temperature of the 2 objects will be the same.
Answer II. is correct.
When 2 objects achieve thermal equilibrium, the rate of flow of heat is equal, hence there is no net flow of heat between the 2 objects.
Answer III. is correct.
When P and Q are in thermal contact, the temperature of P (10°C)will increase whereas the temperature of Q (50°C) will decrease. When P and Q are in thermal equilibrium the temperature of P and Q will be the same and the temperature will be higher than 10°C but lower than 50°C.
Answer IV. is incorrect.
In thermal equilibrium, there is still heat flow between P and Q.
However, the rate of the heat flow is equal in both direction (P to Q and Q to P), hence the net flow of heat between P and Q is zero.
Applications of Thermal Equilibrium
Oven
- When food such as meat or cake is put in the oven, the heat of the oven is transferred into the food.
- This process will continue until the food is in thermal equilibrium with the air in the oven.
- This happen when the temperature of the food is equal to the temperature of the air in the oven.

Refrigerator
- When food is put in the refrigerator, the heat from the food is transferred into the air of the refrigerator.
- This process is continued until the temperature of the food equal to the temperature of the air in the refrigerator, when thermal equilibrium is reached between the food and the refrigerator.
Thermometer
- Thermometer is placed in contact with the patient’s body.
- If both the body temperature of the patient and that of the mercury (or alcohol) in the clinical thermometer have reached thermal equilibrium, then the temperature of the thermometer is the same as the body temperature, hence the reading of the thermometer shows the body temperature of the patient.

