- The specific latent heat of a substance is the amount of heat requires to change the phase of 1 kg of substance at a constant temperature.
- Specific latent heat is measured in J/kg, if energy is measured in J and mass in kg.For example, specific latent heat of ice is 334000J/kg means 334000 J of energy is needed to convert 1kg of water into ice or vice versa.
Formula: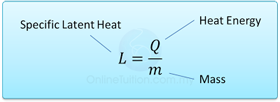
- The specific latent heat of vaporization is the heat needed to change 1 kg of a liquid at its boiling point into vapour without a change in temperature.
- The specific latent heat of fusion is the heat needed to change 1 kg of a solid at its melting point into a liquid, without a change in temperature.
- If any solid is to become a liquid, it must gain the necessary latent heat. Equally, if a liquid is to change back into a solid, it must lose this latent heat.
Measuring the Specific Latent Heat of Fusing of Ice
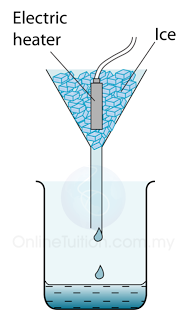
- Figure above shows the apparatus setup to determine the specific latent heat of fusion of ice. Some ice at 0 °C is heated by a small electric heater which is left switched on for several minutes.
- Some of the ice melts to form water which runs down through the funnel and is collected in the beaker.
- The mass of ice (m) melted is found by measuring the mass of water collected.
- If the power of the heater is P and the time taken to heat the ice = t, then the thermal energy supplied by the heater = thermal energy used to melt ice = Pt.
Therefore, the specific latent heat of fusion of ice
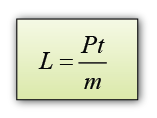
Precaution Steps:
- The heating element of the heater must fully immerse in ice so that all the heat generated is absorbed by the ice.
- A control set is needed to estimate the amount of mass of ice melted by the heat from the surrounding.
Note:
- The heat received by ice is less than the calculated value Pt as some heat is lost to the surrounding. This will result in the value of l obtained from the calculation to be slightly higher than the standard value.
- If impurity is present in water, the melting point of the water will be lower than normal.
Example 1:
How much heat energy is required to change 2 kg of ice at 0°C into water at 20°C? [Specific latent heat of fusion of water = 334 000 J/kg; specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/(kg K).]
Answer:
m = 2kg
Specific latent heat of fusion of water, L = 334 000 J/kg
specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/(kg K)
Energy needed to melt 2kg of ice,
Q1 = mL = (2)(334000) = 668000J
Energy needed to change the temperature from 0°C to °C.
Q2 = mcθ = (2)(4200)(20 - 0) = 168000J
Total energy needed = Q1 + Q2 = 668000 + 168000 = 836000J
How much heat energy is required to change 2 kg of ice at 0°C into water at 20°C? [Specific latent heat of fusion of water = 334 000 J/kg; specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/(kg K).]
Answer:
m = 2kg
Specific latent heat of fusion of water, L = 334 000 J/kg
specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/(kg K)
Energy needed to melt 2kg of ice,
Q1 = mL = (2)(334000) = 668000J
Energy needed to change the temperature from 0°C to °C.
Q2 = mcθ = (2)(4200)(20 - 0) = 168000J
Total energy needed = Q1 + Q2 = 668000 + 168000 = 836000J
Example 2:
Starting at 20°C, how much heat is required to heat 0.3 kg of aluminum to its melting point and then to convert it all to liquid? [Specific heat capacity of aluminium = 900J kg-1 °C-1; Specific latent heat of aluminium = 321,000 Jkg-1, Melting point of aluminium = 660°C]
Answer:
m = 0.3kg
Specific latent heat of fusion of aluminium, L = 321 000 J/kg
specific heat capacity of aluminium = 900 J/(kg K)
Energy needed to increase the temperature from 20°C to 660°C
Q1 = mcθ = (0.3)(900)(660 - 20) = 172,800J
Energy needed to melt 0.3kg of aluminium,
Q2 = mL = (0.3)(321000) = 96,300J
Total energy needed = Q1 + Q2 = 172,800 + 96,300 = 269,100J
Starting at 20°C, how much heat is required to heat 0.3 kg of aluminum to its melting point and then to convert it all to liquid? [Specific heat capacity of aluminium = 900J kg-1 °C-1; Specific latent heat of aluminium = 321,000 Jkg-1, Melting point of aluminium = 660°C]
Answer:
m = 0.3kg
Specific latent heat of fusion of aluminium, L = 321 000 J/kg
specific heat capacity of aluminium = 900 J/(kg K)
Energy needed to increase the temperature from 20°C to 660°C
Q1 = mcθ = (0.3)(900)(660 - 20) = 172,800J
Energy needed to melt 0.3kg of aluminium,
Q2 = mL = (0.3)(321000) = 96,300J
Total energy needed = Q1 + Q2 = 172,800 + 96,300 = 269,100J
Example 3:
How much heat must be removed by a refrigerator from 2 kg of water at 70 °C to convert it to ice cubes at -11°C? [Specific heat capacity of water = 4200J kg-1 °C-1; Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 334,000 Jkg-1, specific heat capacity of ice = 2100 J/(kg K)]
Answer:
m = 2kg
Specific latent heat of fusion of water, L = 334,000 J/kg
Specific heat capacity of water, cw = 4,200 J/(kg K)
Specific heat capacity of ice, ci = 2,100 J/(kg K)
Energy to be removed to reduce the temperature from 70°C to 0°C (Freezing point of water)
Q1 = mcθ = (2)(4200)(70 - 0) = 588,000J
Energy needed to freeze 2kg of water,
Q2 = mL = (2)(334,000) = 668,000J
Energy to be removed to reduce the temperature from 0°C to -11°C
Q3 = mcθ = (2)(2100)(0 - (-11)) = 46,200J
Total energy needed = Q1 + Q2 + Q3 = 588,000 + 668,000 = 46,200J = 1,302,200J
How much heat must be removed by a refrigerator from 2 kg of water at 70 °C to convert it to ice cubes at -11°C? [Specific heat capacity of water = 4200J kg-1 °C-1; Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 334,000 Jkg-1, specific heat capacity of ice = 2100 J/(kg K)]
Answer:
m = 2kg
Specific latent heat of fusion of water, L = 334,000 J/kg
Specific heat capacity of water, cw = 4,200 J/(kg K)
Specific heat capacity of ice, ci = 2,100 J/(kg K)
Energy to be removed to reduce the temperature from 70°C to 0°C (Freezing point of water)
Q1 = mcθ = (2)(4200)(70 - 0) = 588,000J
Energy needed to freeze 2kg of water,
Q2 = mL = (2)(334,000) = 668,000J
Energy to be removed to reduce the temperature from 0°C to -11°C
Q3 = mcθ = (2)(2100)(0 - (-11)) = 46,200J
Total energy needed = Q1 + Q2 + Q3 = 588,000 + 668,000 = 46,200J = 1,302,200J