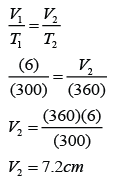Charles’ law states that for a fixed mass of gas, the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas provided the pressure of the gas is kept constant.
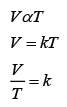
Formula:
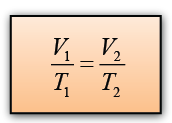
Explanation
- When temperature increases, the average kinetic energy of the gas particles will increase.
- The air molecule move faster and collide with the wall of the container more vigorously at higher frequency.
- As a result, the space between the gas particles increases and the volume of the gas increases.
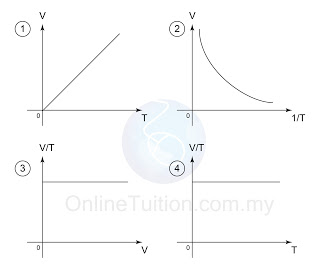
Graph
- In the graphs above, the first graph shows that V is directly proportional to the absolute temperature.
- The second graph shows that, if the temperature is in oC, the graph does not pass through the origin.
- The third and the forth graphs shows that V/T is always constant for all value of V and T.
Example 3:
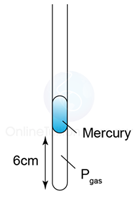

The figure shows some air trapped in a capillary tube. Given that the temperature of the air is 27°C. Find the length of the air column when the temperature of the air is increased to 87°C.
Answer:
V1 = 6cm
T1 = 273 + 27 = 300K
V2 = ?
T2 = 273 + 87 = 360K