Speed of Water Waves
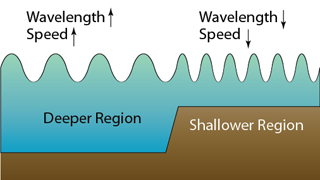
- When straight waves pass from deep to shallow water, their
- wave-length becomes shorter
- speed decreases
- frequency remain unchanged
- This can be illustrated by placing a piece of rectangular Perspex of suitable thickness in the tank to reduce the local water depth.
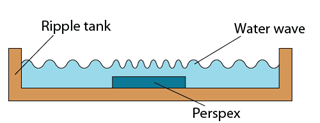
- Figure below shows the wavefront diagram of the wave formed.
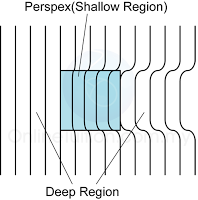
- We can see that the wavelength above the Perspex is shallower.
- The relationship between the speed and wavelength of the wave in deep and shallow region is given by the formula below.
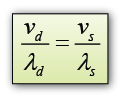
-
vd = speed of wave in deep regionλd = speed of wave in deep regionvs = speed of wave in deep regionλs = speed of wave in deep region
Refraction of Waves at a Boundary
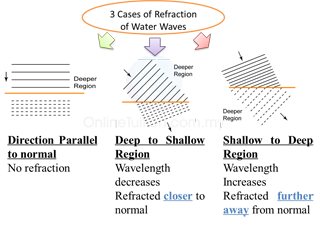
- Refraction is the change in direction of propagation when a wave moves from one medium to another medium.
- It is caused by the change of the speed of the wave when moving from one medium to another.
- For water waves, refraction occurs when the waves move from one region to another region of different depth.
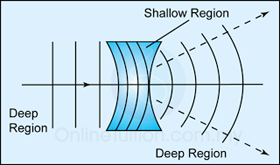
- If water waves pass through a shallow region of convex shape, the waves will be converged.
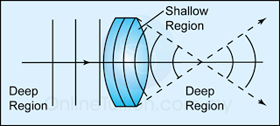
- If water waves pass through a shallow region of concave shape, the waves will be diverged.