- The resistance R of a material is defined as the ratio V : I, where V is the potential difference across the material and I is the current flowing in it.

- The SI unit of resistance is the ohm (W). One ohm is the resistance of a material through which a current of one ampere flows when a potential difference of one volt is maintained.
Finding Resistance from the Potential Difference - Current Graph
In the graph potential difference against current, the gradient of the graph is equal to the resistance of the resistor.
Resistance, R = Gradient of the Graph
Example:
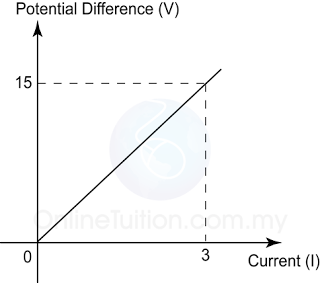

Figure above shows the graph of potential difference across a wire against its current. Find the resistance of the wire.
Answer:
Resistance
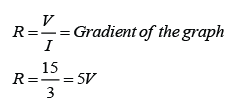
Ohmic Conductor
- Conductors that obey Ohm’s law are said to be ohmic conductor.
- Examples of Ohmic conductor: Metal, Copper sulphate solution with copper electrodes
Non-Ohmic Conductor
- Conductors which do not obey Ohm’s law are called non-ohmic conductor.
- Example: Semiconductor Diode, Vacuum tube diode
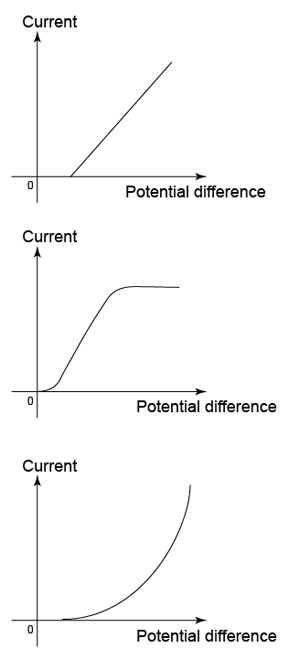 |
| (Examples of characteristic of non-Ohmic conductor) |