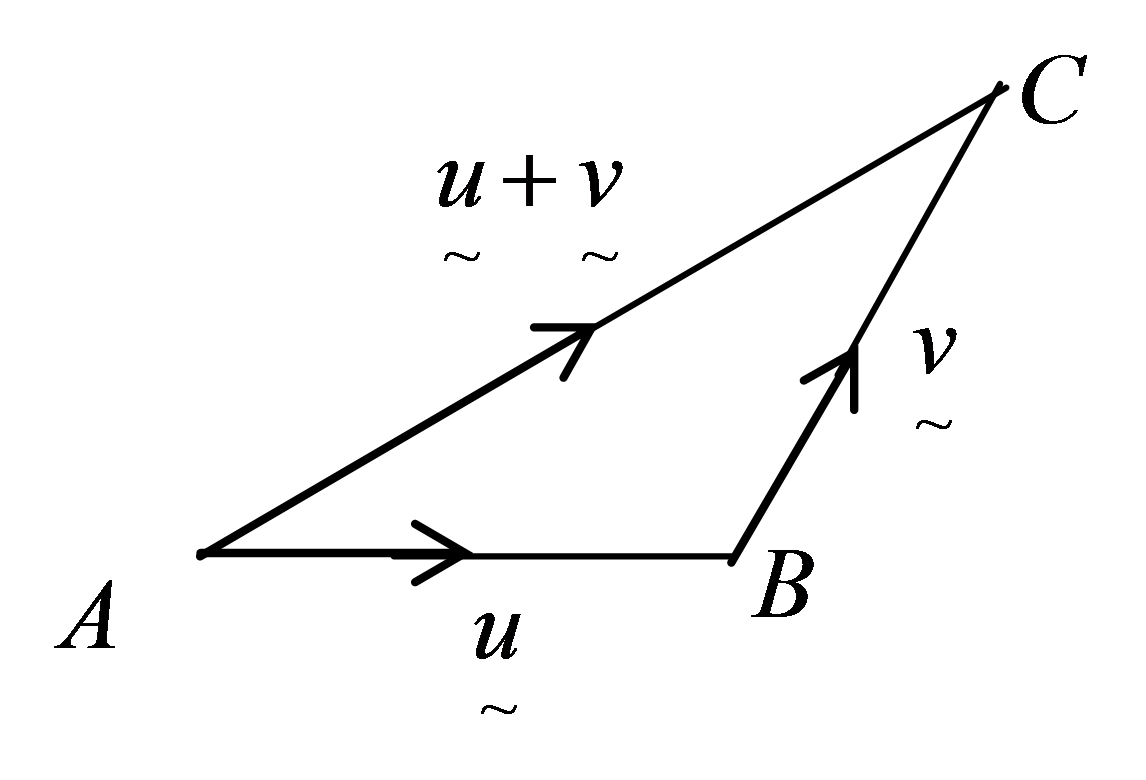4.3 Addition and Subtraction of Vectors
4.3.1 Addition of Vectors
1. The addition of two vectors,
u˜ and v˜
, can be written as
u˜+v˜
. The result of this addition is a vector which is called the resultant vector.
2. When two vectors with the same direction is added up, the resultant vector has
2. When two vectors with the same direction is added up, the resultant vector has
(a) the same direction with both the vectors.
(b) a magnitude equal to the sum of the magnitudes of both the vectors.
Addition of Non-parallel Vectors
1. Addition of two non-parallel vectors,
u˜ and v˜
, can be shown by using two laws.
(a) Triangle Law of Addition
The resultant vector
u˜+v˜
is represented by the third side AC.
(b) Parallelogram Law of Addition
(b) Parallelogram Law of Addition
The resultant vector
u˜+v˜
is represented by the third side AC.