Question 3:
Solution:
(b)
For x-intercept, y = 0
Diagram below shows a straight line JK and a straight line ST drawn on a Cartesian plane. JK is parallel to ST.
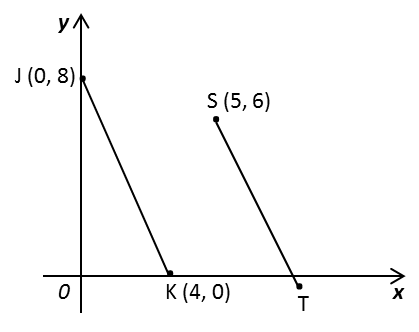

Find
(a) the equation of the straight ST,
(b) the x-intercept of the straight line ST.
Solution:
(a)
JK is parallel to ST, therefore gradient of JK = gradient of ST.
=8−00−4=−2
JK is parallel to ST, therefore gradient of JK = gradient of ST.
Substitute m = –2 and S (5, 6) into y = mx + c
6 = –2 (5) + c
c = 16
Therefore equation of ST: y = –2x + 16
(b)
For x-intercept, y = 0
0 = –2x + 16
2x = 16
x = 8
Therefore x-intercept of ST = 8
Question 4:
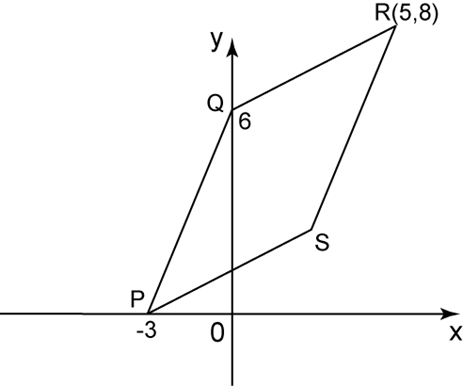
In the diagram above, PQRS is a parallelogram. Find
Solution:
(b)
Gradient of QR=8−65−0=25Substitute m=25 and R (5,8) into y=mx+c8=25(5)+cc=6Therefore equation of QR: y=25x+6
(c)
For x-intercept,y=00=25x+6x=−15

In the diagram above, PQRS is a parallelogram. Find
(a) the gradient of SR,
(b) the equation of QR,
(c) the x-intercept of QR.
Solution:
(a)
PQ is parallel to SR, gradient of PQ = gradient of SR.
Gradient of SR=−6−3=2
PQ is parallel to SR, gradient of PQ = gradient of SR.
Gradient of SR=−6−3=2
(b)
Gradient of QR=8−65−0=25Substitute m=25 and R (5,8) into y=mx+c8=25(5)+cc=6Therefore equation of QR: y=25x+6
(c)
Therefore x-intercept of QR = –15.