- On the surface of the earth, there is a thick layer of gas called the atmosphere. The atmosphere consists of various types of gas called the atmospheric gas.
- The atmospheric gases collide on the surface of the earth and hence exert a pressure on the surface of the earth, called the atmospheric pressure.
- The atmospheric pressure can be measured in the unit of atm, mmHg or Pa. The atmospheric pressure at sea level is taken to be 1 atm, which is approximately 760 mmHg or 101,000 Pa.
Characteristics of Atmospherics Pressure
- Decreases with altitude
The atmospheric pressure changes accordingly to the altitude. Altitude is the height above sea level. The greater the altitude, the lower the atmospheric pressure. - Act equally in all direction
The atmospheric pressure acts on every object in the atmosphere. It acts equally in all direction. - Atmospheric pressure is ~ 100,000Pa at sea level
On the surface of the earth, the atmospheric pressure can be as high as 101,000 Pa.
Unit Used to Measure Atmospheric Pressure
- The following are the unit used to measure atmospheric pressure
- Pascal (Pa)
1 Pa = 1 N/m² - Standard Atmospheric Pressure (atm)
1 atm = Atmospheric Pressure at sea level ( = 101,325 Pa) - mmHg (also known as torr)
1 mmHg = 1/760 atm (roughly equal to the liquid pressure exerted by a millimetre of mercury). - milibar (Not used in SPM)
- Pascal (Pa)
- In SPM, usually we use the unit cmHg, instead of mmHg.
Proof of Existence of Atmospheric Pressure
The existence of the atmospheric pressure can be proved by the following experiments.- Crushing can experiment
- Water cover with cardboard does not flow out
- Magdeburg Hemisphere
Crushing Can Experiment
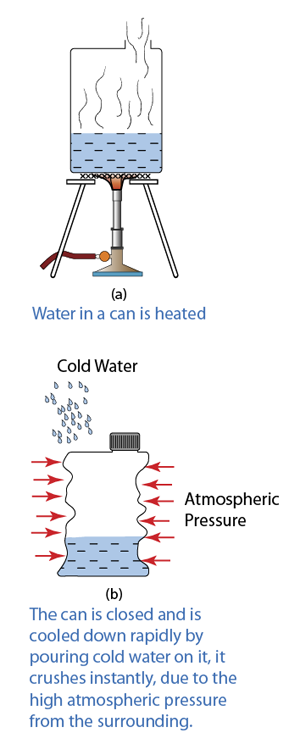
- When a can filled with hot water is closed and is cooled down rapidly by pouring cold water on it, it will crush instantly.
- This experiment proves that there is a huge atmospheric pressure exerts on everything on the surface of the earth.
Water cover with cardboard does not flow out
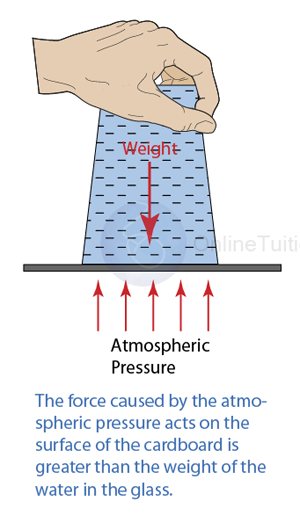
- The cardboard does not fall and the water remains in the glass even though it's not supported by anything.
- This is because the force caused by the atmospheric pressure acts on the surface of the cardboard is greater than the weight of the water in the glass. This experiment proves that atmospheric pressure is present on the surface of the earth.
Magdeburg Hemisphere
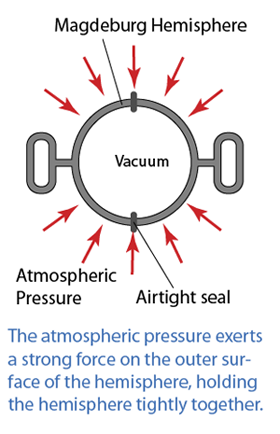
- When the air inside the hemisphere is pumped out so that it becomes a vacuum, the hemisphere cannot be separated even by a very great force.
- This is because when the air is pumped out, the pressure inside the hemisphere becomes very low.
- The atmospheric pressure exerts a strong force on the outer surface of the hemisphere, holding the hemisphere tightly together.