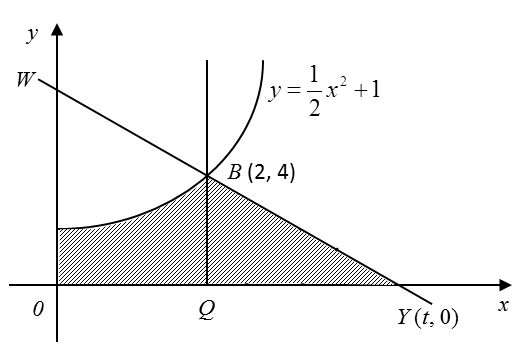
Question 1:
Solution:
(a)
(b)
(c)
A curve with gradient function
has a turning point at (m, 9).
(a) Find the value of m.
(b) Determine whether the turning point is a maximum or a minimum point.
(c) Find the equation of the curve.
(c) Find the equation of the curve.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Question 2:
Solution:
(a)
A curve has a gradient function kx2– 7x, where k is a constant. The tangent to the curve at the point (1, 3 ) is parallel to the straight line y + x– 4 = 0.
Find
(a) the value of k,
(b) the equation of the curve.
(a)
y + x – 4 = 0
y = – x + 4
m = –1
f ’(x) = kx² – 7x
Given tangent to the curve at the point (1, 3) parallel to the straight line
k (1)² – 7 (1) = –1
k – 7 = –1
k = 6
(b)