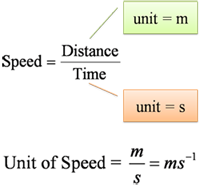
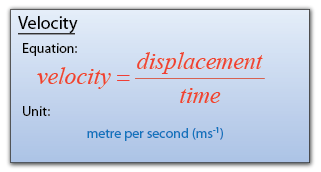
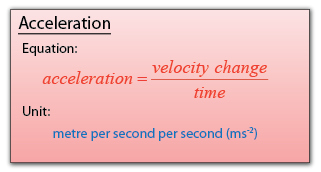
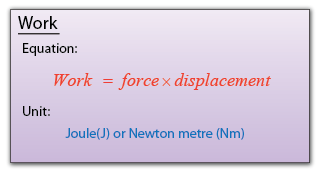
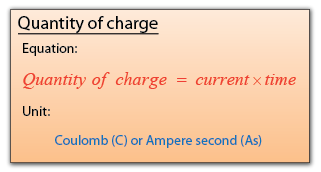
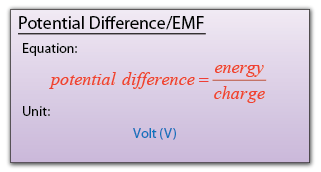
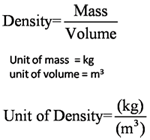Speed, density and pressure are derived quantities. When converting their units, firstly, we write the units in fraction form, then only do the unit convertion for the numerator and denominator.
Example
1. Complete the following unit conversion of speed.
a.
1. Complete the following unit conversion of speed.
- 90 kmh-1 = __________ ms-1
- 110 kmh-1 = __________ ms-1
- 1.3 ms-1 = __________ kmh-1
- 8.12 ms-1 = __________ kmh-1
a.
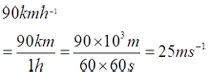
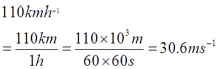
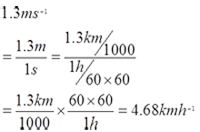
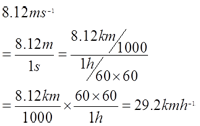
2. Complete the following unit conversion of density and pressure.
- 760 kgm-3 = __________ gcm-3
- 12000 kgm-3 = __________ gcm-3
- 5.1 gcm-3 = __________ kgm-3
- 3600 Nm-2 = __________ Ncm-2
- 12x106 Nm-2 = __________ Ncm-2
- 1.5x103 Nm-2= __________ Ncm-2
- 3.16x10-5 Ncm-2= __________ Nm-2
- 7.1x10-3 Ncm-2 = __________ Nm-2
Answer:
a.
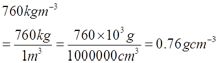
b.
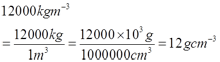
c.
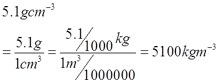
d.
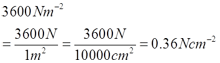
e.
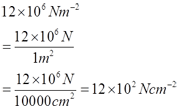
f.
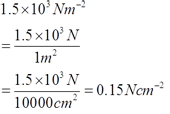
g.
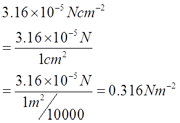
h.