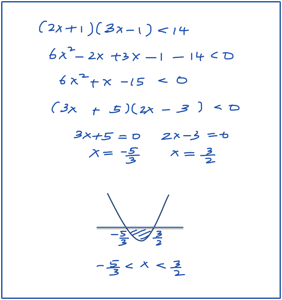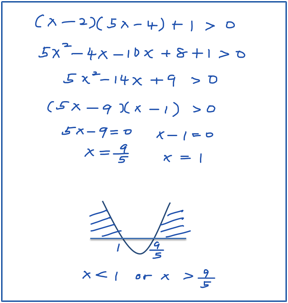(C) Linear Inequality
Example 1:
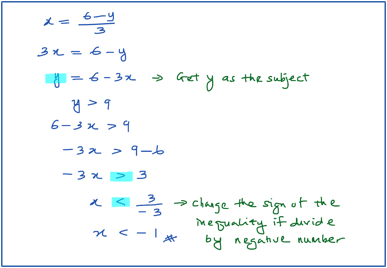
- Givenfind the range of values of x for which y > 9.
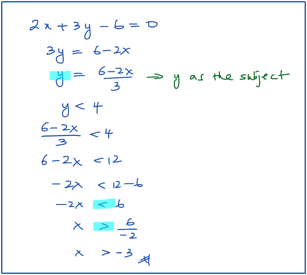
- Given 2x + 3y – 6 =0, find the range of values of x for which y < 4.
Solution:
(D) Quadratic Inequality
Example 2:
Find the range of values of x which satisfy the following inequalities:
- (2x + 1) (3x – 1) < 14
- (x – 2) (5x – 4) + 1 > 0
Solution: