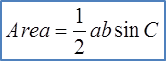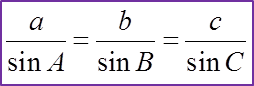Question 3:
Solution:
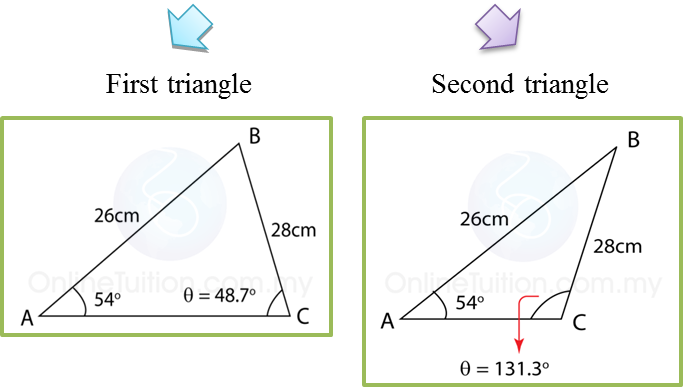
(a)
QSsinP=PSsinQQSsin85∘=13.1sin28∘QS=13.1×sin85∘sin28∘QS=27.8 cm
(b)
∠RQS = 180o – 85o – 28o
(c)
Using cosine rule,QS2=QR2+RS2−2(QR)(RS)cos∠QRS27.82=6.42+25.982−2(6.4)(25.98)cos∠QRS772.84=715.92−332.54cos∠QRScos∠QRS=715.92−772.84332.54cos∠QRS=−0.1712∠QRS=99.86∘
(d)
Area of triangle QRS

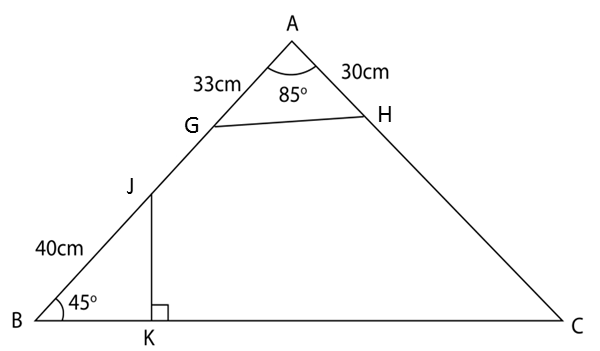
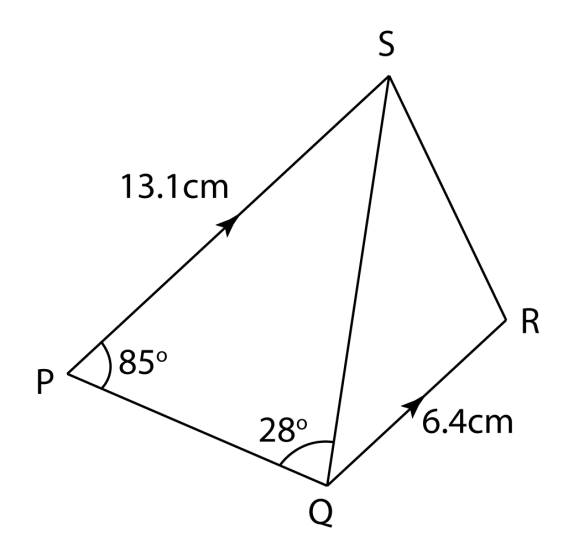
The diagram shows a trapezium PQRS. PS is parallel to QR and QRS is obtuse. Find
(a) the length, in cm, of QS,
(b) the length, in cm, of RS,
(c) ∠QRS,
(d) the area, in cm2, of triangle QRS.
(a)
QSsinP=PSsinQQSsin85∘=13.1sin28∘QS=13.1×sin85∘sin28∘QS=27.8 cm
(b)
∠RQS = 180o – 85o – 28o
∠RQS = 67o
Using cosine rule,
RS2 = QR2 + QS2 – 2 (QR)(QS) ∠RQS
RS2 = 6.42 + 27.82 – 2 (6.4)(27.8) cos 67o
RS2 = 813.8 – 139.04
RS2 = 674.76
RS = 25.98 cm
(c)
Using cosine rule,QS2=QR2+RS2−2(QR)(RS)cos∠QRS27.82=6.42+25.982−2(6.4)(25.98)cos∠QRS772.84=715.92−332.54cos∠QRScos∠QRS=715.92−772.84332.54cos∠QRS=−0.1712∠QRS=99.86∘
(d)
Area of triangle QRS
= ½ (QR)(RS) sin R
= ½ (6.4) (25.98) sin 99.86o
= 81.91 cm2