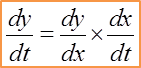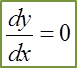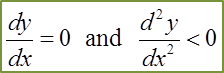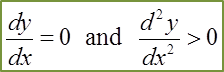Question 1:
Solution:
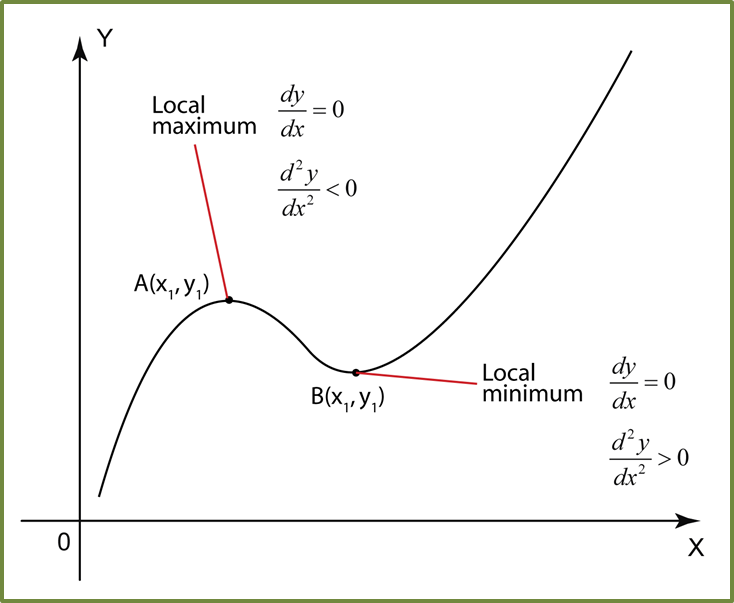
The curve y = x3 – 6x2 + 9x + 3 passes through the point P (2, 5) and has two turning points, A (3, 3) and B.
Find
(a) the gradient of the curve at P.
(b) the equation of the normal to the curve at P.
(c) the coordinates of B and determine whether B is a maximum or the minimum point.
Solution:
(a)
y = x3 – 6x2 + 9x + 3
dy/dx = 3x2– 12x + 9
At point P (2, 5),
dy/dx = 3(2)2 – 12(2) + 9 = –3
Gradient of the curve at point P = –3.
(b)
Gradient of normal at point P = 1/3
Equation of the normal at P (2, 5):
y – y1 = m (x – x1)
y – 5 = 1/3 (x – 2)
3y – 15 = x – 2
3y = x + 13
(c)
At turning point, dy/dx = 0.
3x2 – 12x + 9 = 0
x2 – 4x + 3 = 0
(x – 1)( x – 3) = 0
x – 1 = 0 or x – 3 = 0
x = 1 x = 3 (Point A)
Thus at point B:
x = 1
y = (1)3– 6(1)2 + 9(1) + 3 = 7
Thus, coordinates of B = (1, 7)