3.9.1 Quadratic Functions, SPM Practice (Long Questions)
Question 1:
Without drawing graph or using method of differentiation, find the maximum or minimum value of the function y = 2 + 4x – 3x2. Hence, find the equation of the axis of symmetry of the graph.
Solution:
By completing the square for the function in the form of y = a(x + p)2+ q to find the maximum or minimum value of the function.
y = 2 + 4x – 3x2
y = – 3x2 + 4x + 2 ← (in general form)
Since a = –3 < 0,
Therefore, the function y has a maximum value of
Equation of the axis of symmetry of the graph is
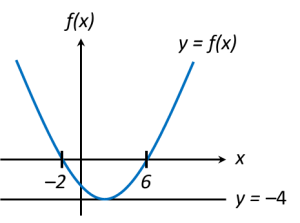
The diagram above shows the graph of a quadratic function y = f(x). The straight line y = –4 is tangent to the curve y = f(x).
(a) Write the equation of the axis of symmetry of the function f(x).
(b) Express f(x) in the form of (x + p)2 + q , where p and q are constant.
(c) Find the range of values of x so that
(i) f(x) < 0, (ii) f(x) ≥ 0.
Solution:
(a)
x-coordinate of the minimum point is the midpoint of (–2, 0) and (6, 0)
=
Therefore, equation of the axis of symmetry of the function f(x) is x = 2.
(b)
Substitute x = 2 into x + p = 0,
2 + p = 0
p = –2
and q = –4 (the smallest value of f(x))
Therefore, f(x) = (x + p)2 + q
f(x) = (x – 2)2 – 4
(c)(i) From the graph, for f(x) < 0, range of values of x are –2 < x < 6 ← (below x-axis).
(c)(ii) From the graph, for f(x) ≥ 0, range of values of x are x ≤ –2 or x ≥ 6 ← (above x-axis).