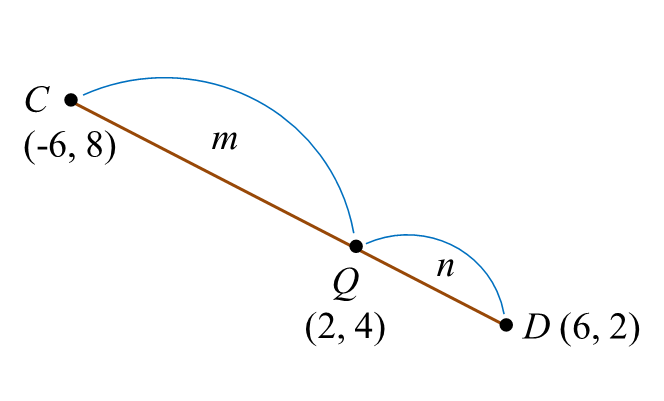
Question 9 (7 marks):
Diagram shows the plan of a rectangular garden ABCD. The garden consists of a semicircular pond ATD and grassy area ABCDT.
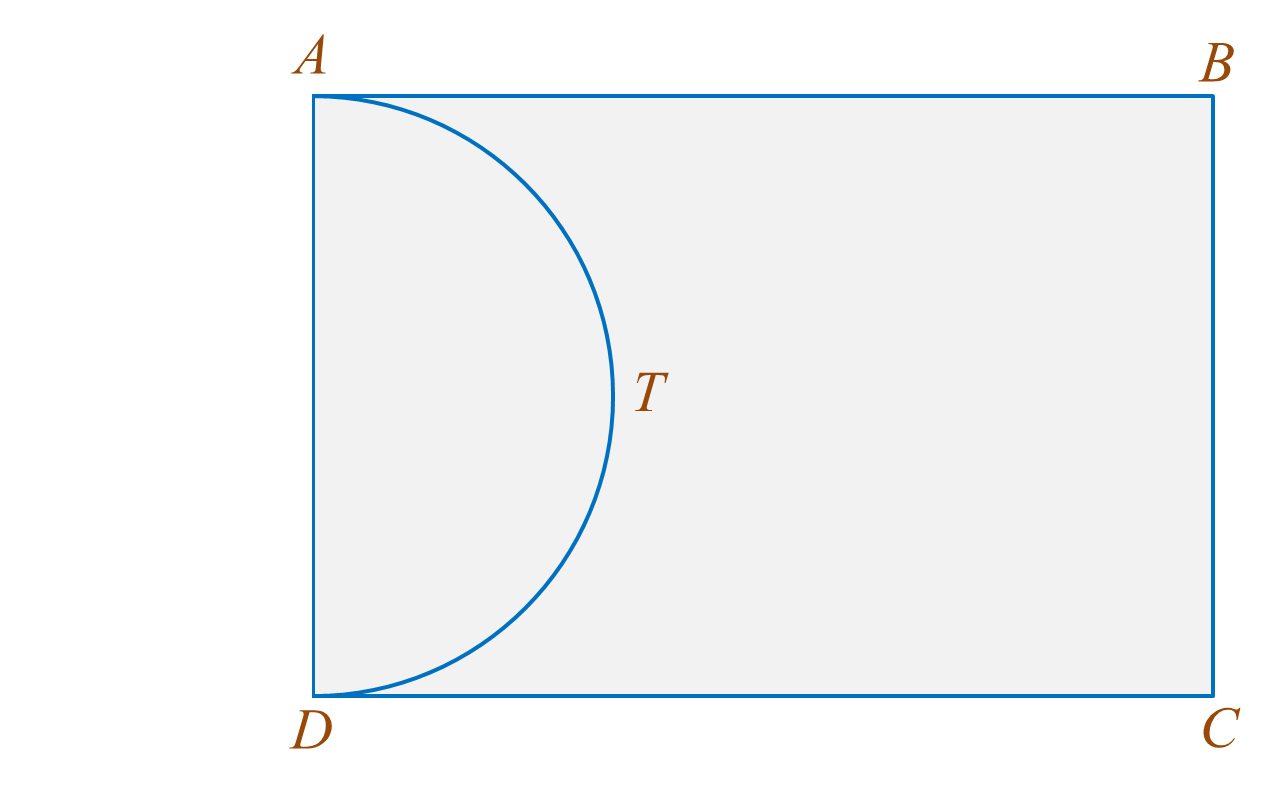 It is given that DC = 6y metre and BC = 7x metre, x ≠ y. The area of the rectangular garden ABCD is 168 metre2 and the perimeter of the grassy area is 60 metre. The pond with uniform depth contains 15.4 metre3 of water.
It is given that DC = 6y metre and BC = 7x metre, x ≠ y. The area of the rectangular garden ABCD is 168 metre2 and the perimeter of the grassy area is 60 metre. The pond with uniform depth contains 15.4 metre3 of water.
By using , find the depth, in metre, of water in the pond.
Solution:
Diagram shows the plan of a rectangular garden ABCD. The garden consists of a semicircular pond ATD and grassy area ABCDT.
 It is given that DC = 6y metre and BC = 7x metre, x ≠ y. The area of the rectangular garden ABCD is 168 metre2 and the perimeter of the grassy area is 60 metre. The pond with uniform depth contains 15.4 metre3 of water.
It is given that DC = 6y metre and BC = 7x metre, x ≠ y. The area of the rectangular garden ABCD is 168 metre2 and the perimeter of the grassy area is 60 metre. The pond with uniform depth contains 15.4 metre3 of water.By using , find the depth, in metre, of water in the pond.
Solution:
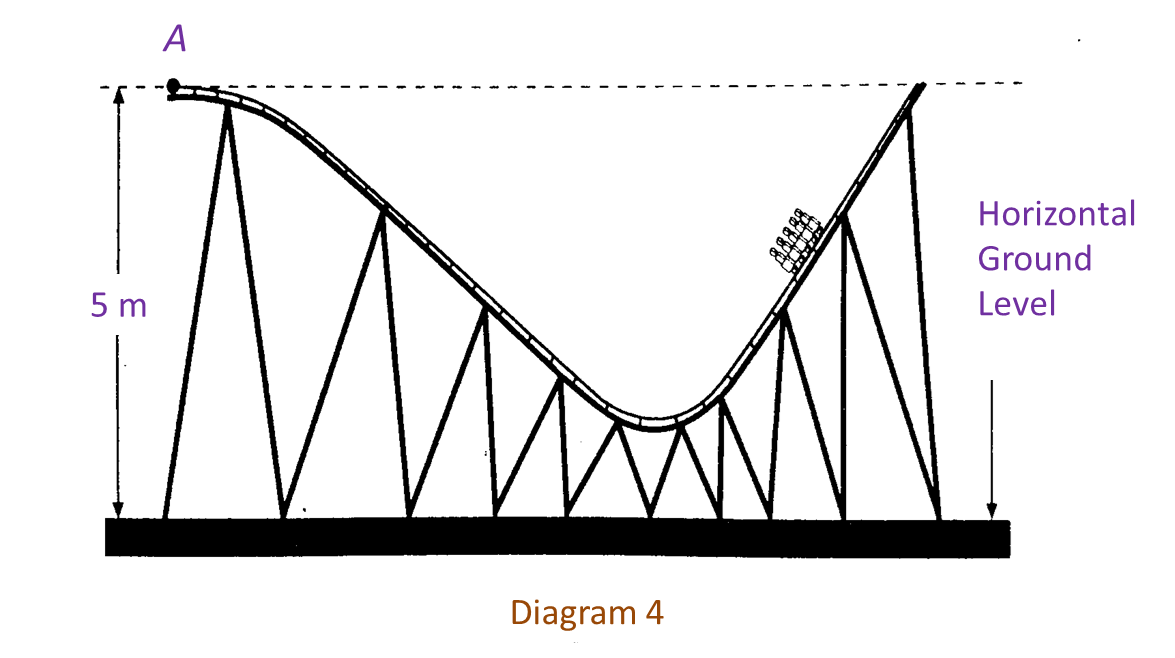
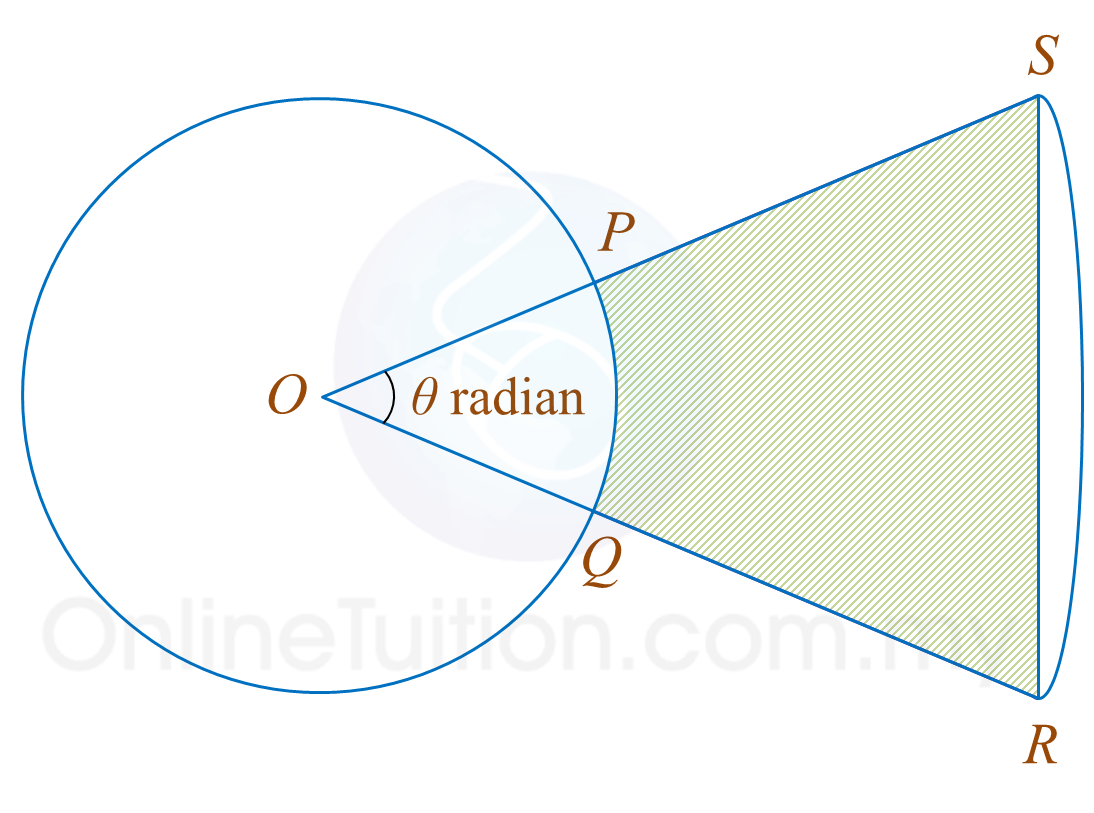


 Diagram
Diagram