Question 7:
The diagram below shows the graph of the quadratic function f(x) = (x + 3)2 + 2h – 6, where h is a constant.
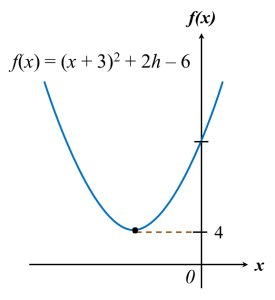
(a) State the equation of the axis of symmetry of the curve.
(b) Given the minimum value of the function is 4, find the value of h.
Solution:
(a)
When x + 3 = 0
x = –3
Therefore, equation of the axis of symmetry of the curve is x = –3.
(b)
When x + 3 = 0, f(x) = 2h – 6
Minimum value of f(x) is 2h – 6.
2h – 6 = 4
2h = 10
h = 5
The diagram below shows the graph of the quadratic function f(x) = (x + 3)2 + 2h – 6, where h is a constant.

(a) State the equation of the axis of symmetry of the curve.
(b) Given the minimum value of the function is 4, find the value of h.
Solution:
(a)
When x + 3 = 0
x = –3
Therefore, equation of the axis of symmetry of the curve is x = –3.
(b)
When x + 3 = 0, f(x) = 2h – 6
Minimum value of f(x) is 2h – 6.
2h – 6 = 4
2h = 10
h = 5
Question 8 (4 marks):
The quadratic function f is defined by f(x) = x2 + 4x + h, where h is a constant.
(a) Express f(x) in the form (x + m)2 + n, where m and n are constants.
(b) Given the minimum value of f(x) is 8, find the value of h.
Solution:
(a)
f(x) = x2 + 4x + h
= x2 + 4x + (2)2 – (2)2 + h
= (x + 2)2 – 4 + h
(b)
Given the minimum value of f(x) = 8
– 4 + h = 8
h = 12
The quadratic function f is defined by f(x) = x2 + 4x + h, where h is a constant.
(a) Express f(x) in the form (x + m)2 + n, where m and n are constants.
(b) Given the minimum value of f(x) is 8, find the value of h.
Solution:
(a)
f(x) = x2 + 4x + h
= x2 + 4x + (2)2 – (2)2 + h
= (x + 2)2 – 4 + h
(b)
Given the minimum value of f(x) = 8
– 4 + h = 8
h = 12
Question 9 (3 marks):
Find the range of values of x such that the quadratic function f(x) = 6 + 5x – x2 is negative.
Solution:
(a)
f(x) < 0
6 + 5x – x2 < 0
(6 – x)(x + 1) < 0
x < –1, x > 6
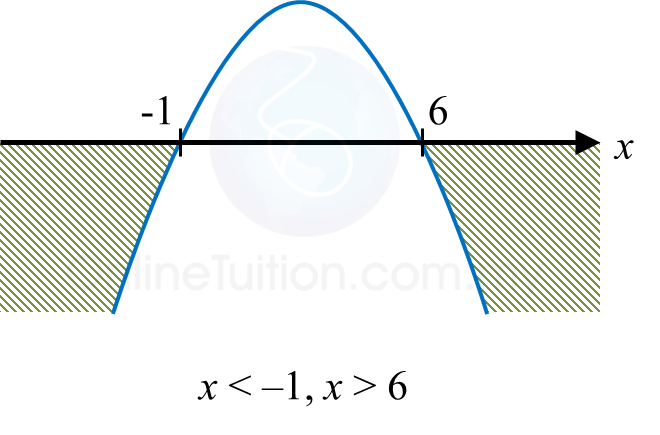
Find the range of values of x such that the quadratic function f(x) = 6 + 5x – x2 is negative.
Solution:
(a)
f(x) < 0
6 + 5x – x2 < 0
(6 – x)(x + 1) < 0
x < –1, x > 6


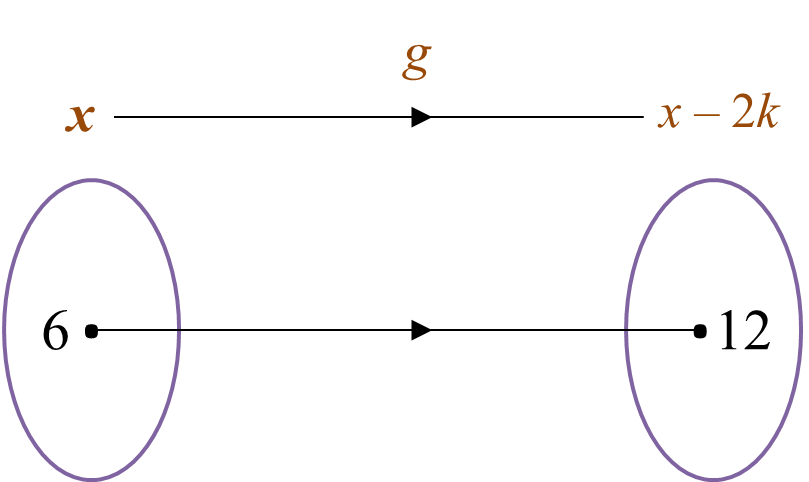
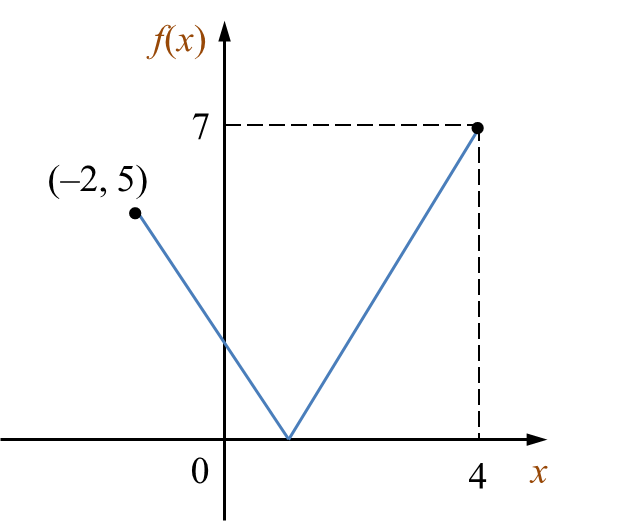 Diagram
Diagram 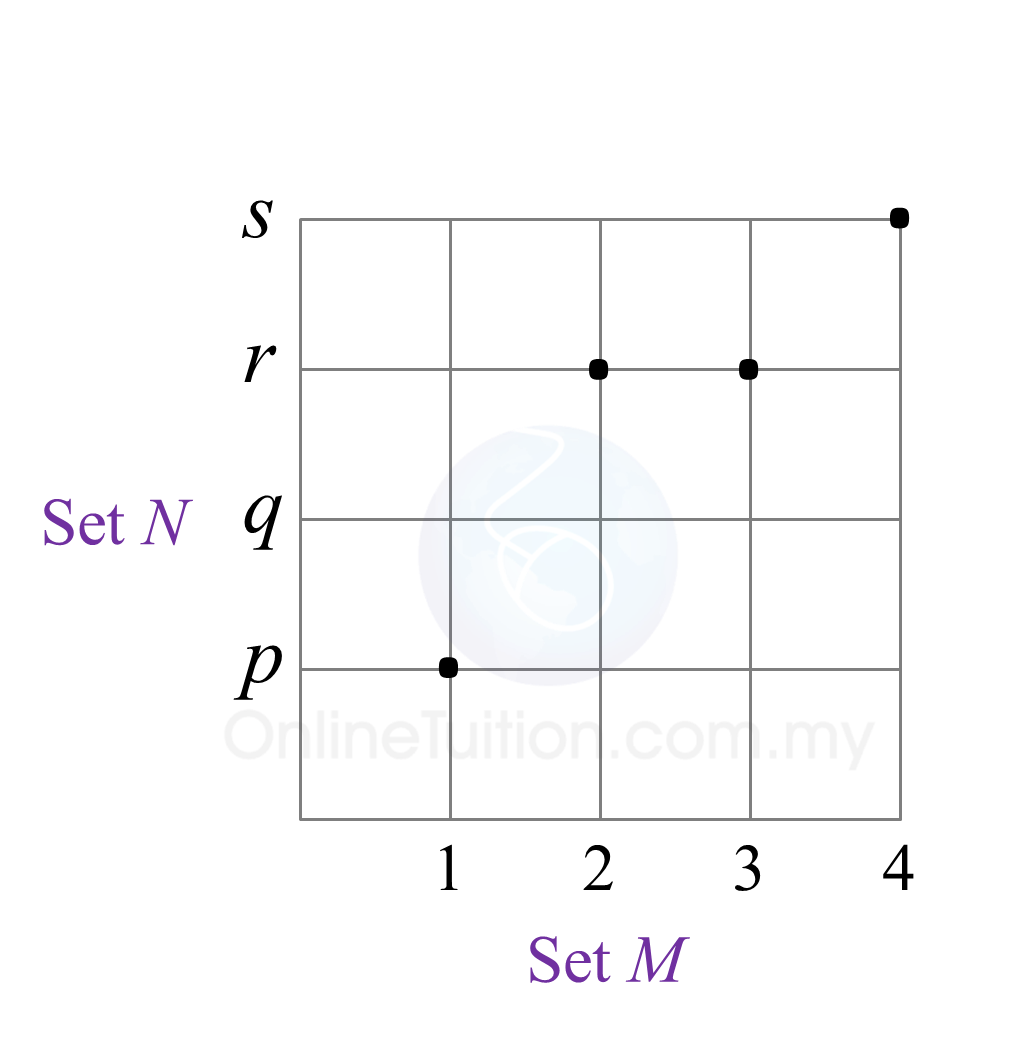 State
State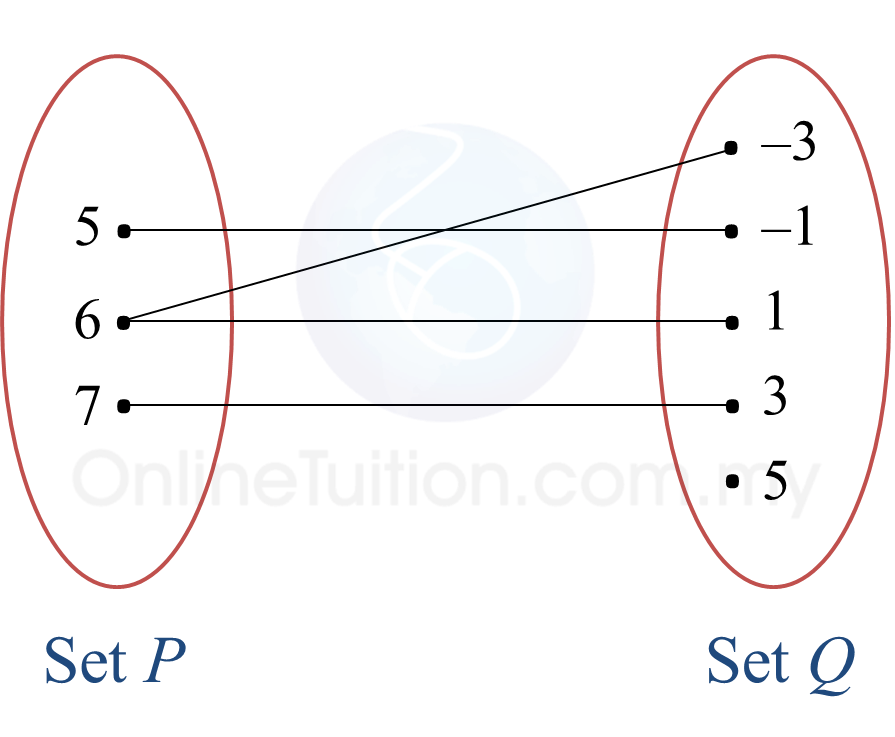

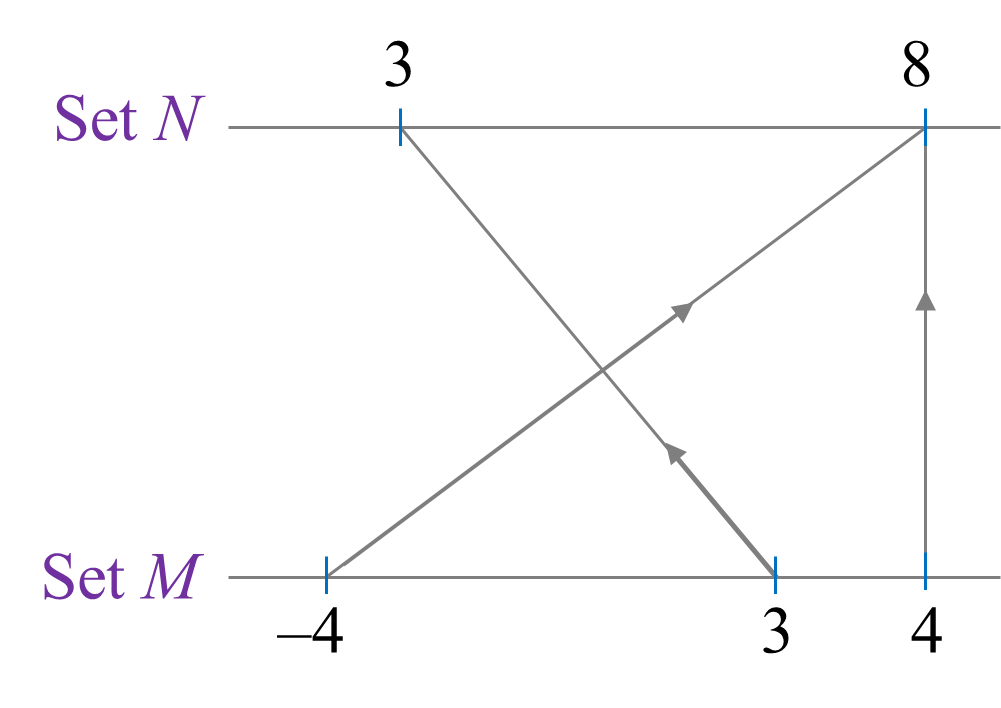
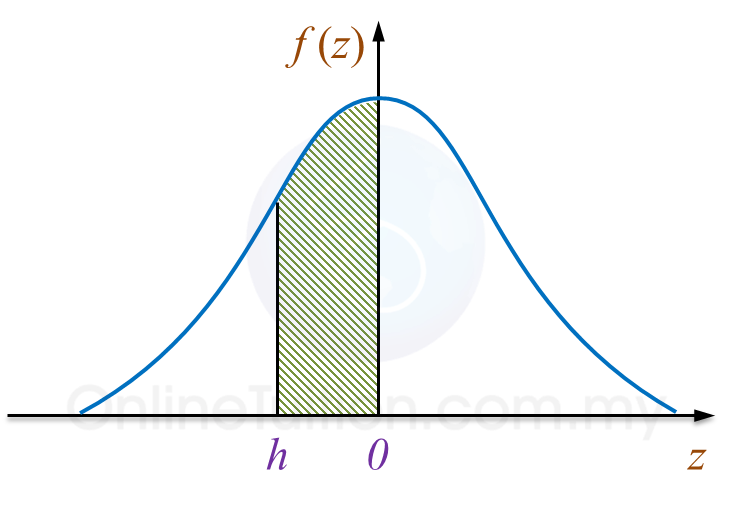 Rajah
Rajah 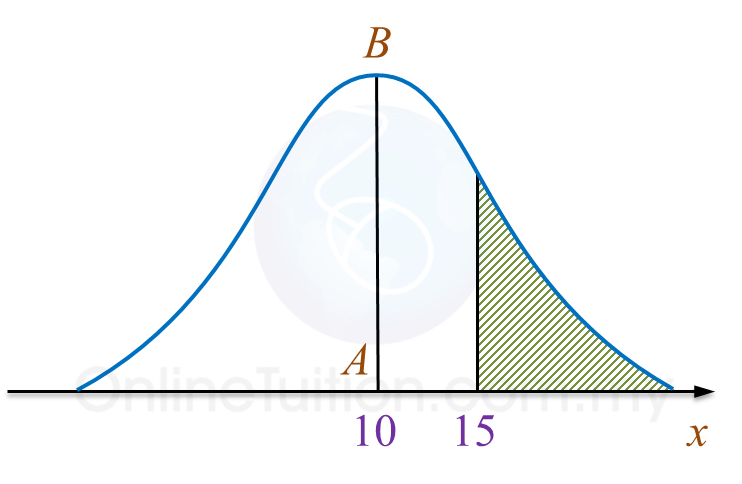 Rajah
Rajah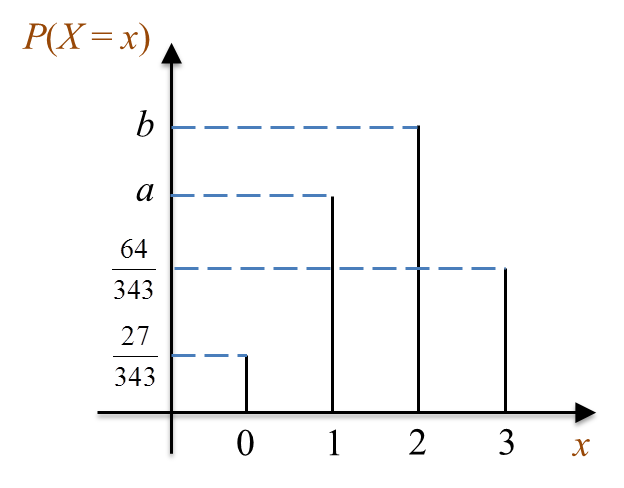 Rajah
Rajah