Question 5:
Diagram below shows a quadrilateral ABCD. Point C lies on the y-axis.
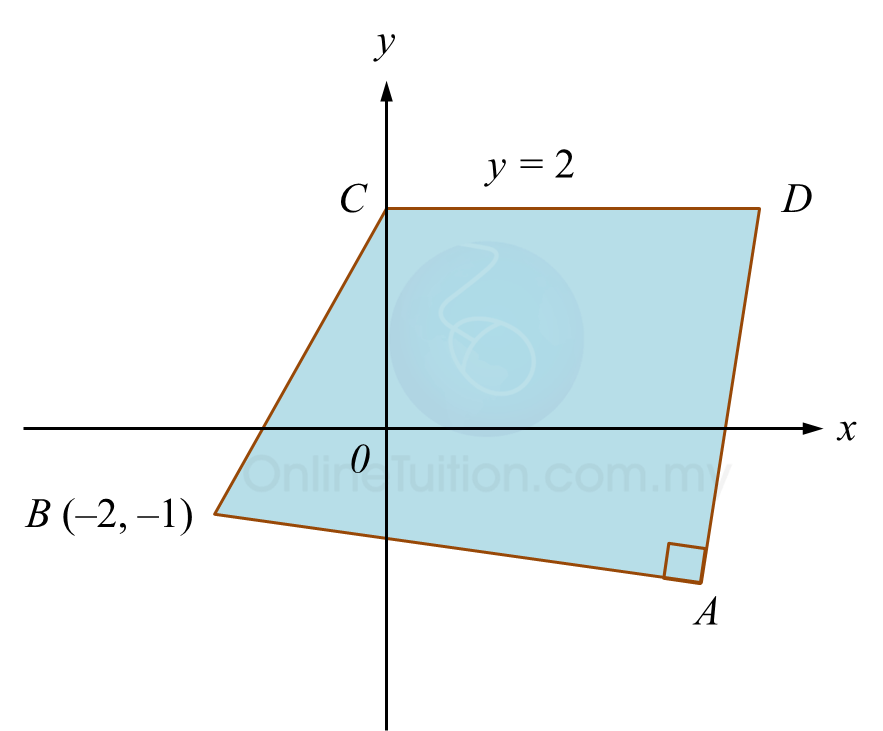
The equation of a straight line AD is 2y = 5x – 21
(a) Find
(i) the equation of the straight line AB,
(ii) the coordinates of A,
(b) A point P moves such that its distance from point D is always 5 units.
Find the equation of the locus of P.
Solution:
(a)(i)
2y=5x−21y=52x−212mAD=52mAB×mAD=−1mAB×52=−1mAB=−25Equation of ABy−y1=mAB(x−x1)y+1=−25(x+2)5y+5=−2x−45y=−2x−9
(a)(ii)
2y=5x−21 .......... (1)5y=−2x−9 .......... (2)(1)×5:10y=25x−105 .......... (3)(2)×2:10y=−4x−18 .......... (4)(2)−(4):0=29x−87x=3From (1),2y=15−212y=−6y=−3A=(3 , −3)
(b)
y=2,4=5x−215x=25x=5Point D=(5, 2)PD=5√(x−5)2+(y−2)2=5(x−5)2+(y−2)2=25x2−10x+25+(y2−4y+4)=25x2+y2−10x−4y+4=0
Diagram below shows a quadrilateral ABCD. Point C lies on the y-axis.

The equation of a straight line AD is 2y = 5x – 21
(a) Find
(i) the equation of the straight line AB,
(ii) the coordinates of A,
(b) A point P moves such that its distance from point D is always 5 units.
Find the equation of the locus of P.
Solution:
(a)(i)
2y=5x−21y=52x−212mAD=52mAB×mAD=−1mAB×52=−1mAB=−25Equation of ABy−y1=mAB(x−x1)y+1=−25(x+2)5y+5=−2x−45y=−2x−9
(a)(ii)
2y=5x−21 .......... (1)5y=−2x−9 .......... (2)(1)×5:10y=25x−105 .......... (3)(2)×2:10y=−4x−18 .......... (4)(2)−(4):0=29x−87x=3From (1),2y=15−212y=−6y=−3A=(3 , −3)
(b)
y=2,4=5x−215x=25x=5Point D=(5, 2)PD=5√(x−5)2+(y−2)2=5(x−5)2+(y−2)2=25x2−10x+25+(y2−4y+4)=25x2+y2−10x−4y+4=0