Question 1:
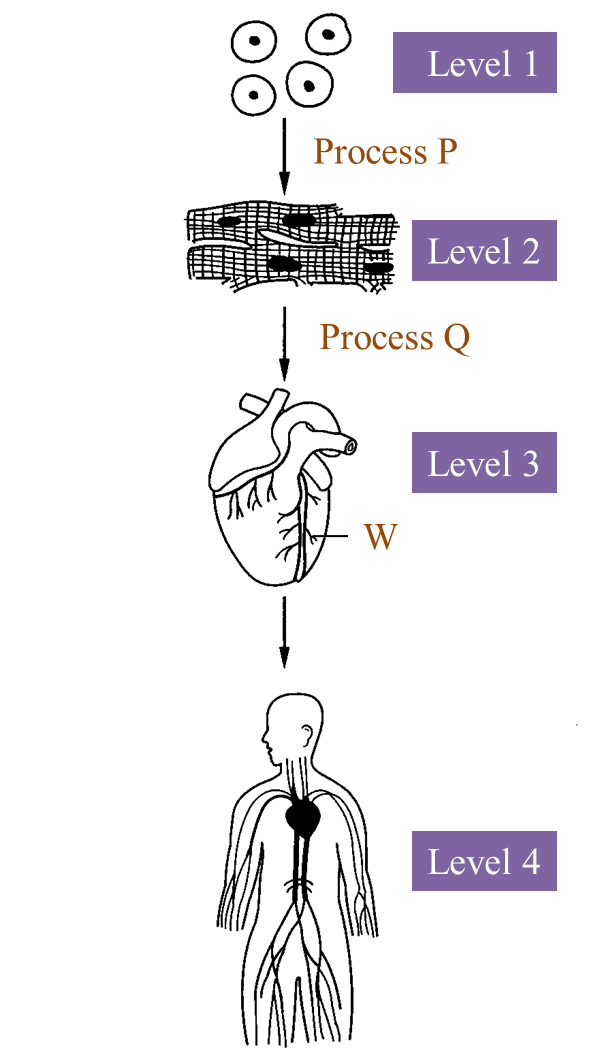
Diagram below shows four levels of cell organization in humans.
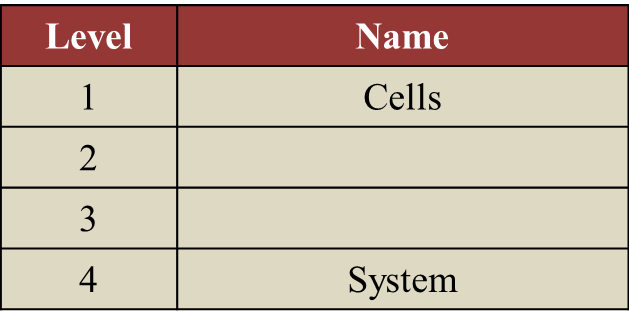
(a) Complete Table below by naming Level 2 and Level 3. [2 marks]
(b)(i) The cells undergo process P to become specific cells that perform a specific function.
Name process P. [1 mark]
(ii) What is the function of the structure in level 2? [1 mark]
(iii) The structure in level 4 is one of the body systems.
Name this system. [1 mark]
(iv) State one function of the system in (b)(iii). [1 mark]
(c)(i) Name and explain the condition which can cause a blockage in blood vessel W. [3 marks]
(ii) A person is suffering from the condition in (c)(i).
State three effects on the person’s health. [3 marks]
Answer:
(a)
Level 2: Tissue
Level 3: Organ
(b)(i)
Process P: Differentiation
(b)(ii)
Function: able to contract and relax to pump the blood
(b)(iii)
Blood circulatory system
(b)(iv)
Transport oxygen, nutrients and antibodies
(c)(i)
Thrombosis – Deposition of cholesterol inside the lumen of a blood vessel which clogs the blood vessel.
Or
Embolism – Movement of cholesterol inside a blood vessel which clogs the blood vessel and leads to thrombosis.
Or
Arteriosclerosis – Deposition of cholesterol/ fat/ calcium inside the lumen of a blood vessel which cause narrowing of the lumen and leads to clogging.
(c)(ii)
1. Chest pain
2. Stroke
3. Heart attacks
Diagram below shows four levels of cell organization in humans.

(a) Complete Table below by naming Level 2 and Level 3. [2 marks]

(b)(i) The cells undergo process P to become specific cells that perform a specific function.
Name process P. [1 mark]
(ii) What is the function of the structure in level 2? [1 mark]
(iii) The structure in level 4 is one of the body systems.
Name this system. [1 mark]
(iv) State one function of the system in (b)(iii). [1 mark]
(c)(i) Name and explain the condition which can cause a blockage in blood vessel W. [3 marks]
(ii) A person is suffering from the condition in (c)(i).
State three effects on the person’s health. [3 marks]
Answer:
(a)
Level 2: Tissue
Level 3: Organ
(b)(i)
Process P: Differentiation
(b)(ii)
Function: able to contract and relax to pump the blood
(b)(iii)
Blood circulatory system
(b)(iv)
Transport oxygen, nutrients and antibodies
(c)(i)
Thrombosis – Deposition of cholesterol inside the lumen of a blood vessel which clogs the blood vessel.
Or
Embolism – Movement of cholesterol inside a blood vessel which clogs the blood vessel and leads to thrombosis.
Or
Arteriosclerosis – Deposition of cholesterol/ fat/ calcium inside the lumen of a blood vessel which cause narrowing of the lumen and leads to clogging.
(c)(ii)
1. Chest pain
2. Stroke
3. Heart attacks