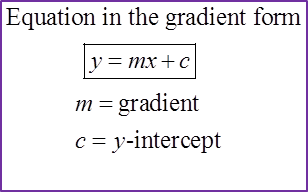
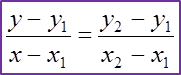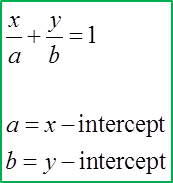6.4.2 Equation of Straight Lines
Case 1
1. The gradient and coordinates of a point are given.
Case 1
1. The gradient and coordinates of a point are given.
2. The equation of a straight line with gradient m passes through the point (x1, y1) is:
Example 1:
A straight line with gradient –3 passes through the point (–1, 5). Find the equation of this line.
Solution:
y – y1 = m (x – x1)
y – 5 = – 3 (x – (–1))
y – 5 = – 3x – 3
y = – 3x + 2
Case 2
1. The coordinates of two points are given.
1. The coordinates of two points are given.
2. The equation of a straight line joining the points (x1, y1)
and (x2, y2) is:
and (x2, y2) is:
Example 2:
Find the equation of the straight line joining the points (2, 4) and (5, 6).
Solution:
y−y1x−x1=y2−y1x2−x1Let (x1,y1)=(2, 4) and (x2,y2) = (5, 6)y−4x−2=6−45−2y−4x−2=233y−12=2x−43y=2x+8
Find the equation of the straight line joining the points (2, 4) and (5, 6).
Solution:
y−y1x−x1=y2−y1x2−x1Let (x1,y1)=(2, 4) and (x2,y2) = (5, 6)y−4x−2=6−45−2y−4x−2=233y−12=2x−43y=2x+8
Case 3
Example 3:
1. The equation of a straight line with x–intercept “a” and y–intercept“b” is:
Example 3:
Find the equation of the straight line joining the points (5, 0) and (0, –6).
Solution:
x–intercept, a = 5, y–intercept, b = –6
Equation of the straight line
xa+yb=1x5+y(−6)=1x5−y6=1