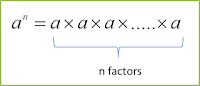Positive Integral Indices
When a real number a is multiplied by itself n times, the result is the nth power of a.
Example: 5×5×5×5 = 54 (5 to the power of 4)
In general, if a is any real number and n is a positive integer, then
The integer n is called the index or exponent and a is the base.
5.1 Indices and Laws of Indices (Part 1)
(A) Zero IndicesThe zero index of any number is equal to one.
a 0 = 1, where a ≠ 0 |
Example 1:
Find the value of the followings:
(a) 2500
(b) 0.5130
(c) (27)0(d) (−11125)0
Solution:
(a) 2500 = 1
(b) 0.5130 = 1
(c) (27)0=1(d) (−11125)0=1
(B) Negative Integral Indices
a−n is a reciprocal of an. a−n=1an
Example 2:
Find the value of the followings:
(a) 102 -1
(b) –6 -3
(c) (13)−4(d) (25)−2(e) −(25)−4
Solution:
(a) 102−1=1102(b) −6−3=1−63=−1216(c) (13)−4=(3)4=81(d) (25)−2=(52)2=254(e) (−25)−4=(−52)4=62516