Measures of Dispersion (Part 2)
7.2b Interquartile Range 2
7.2b Interquartile Range 2
(C) Interquartile Range of Grouped Data (with Class Interval)
The interquartile range of grouped data can be determined by Method 1 (using a cumulative frequency table) or Method 2 (using an ogive).

Example:
The table below shows the marks obtained by a group of Form 4 students in school mathematics test.
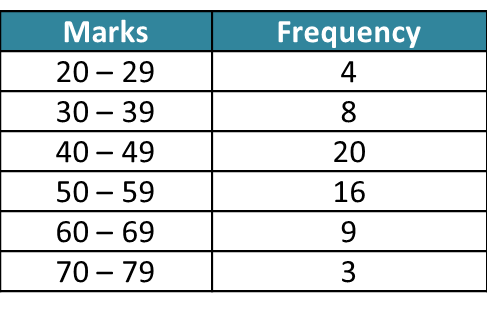
Estimate the interquartile range.
Step 3:
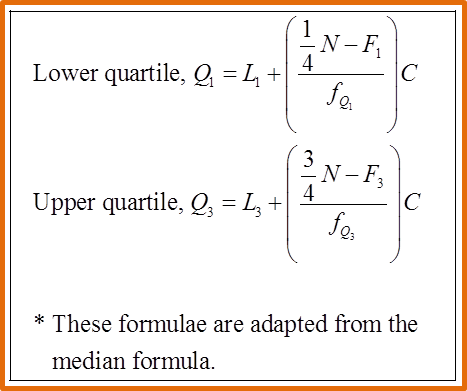
Upper quartile, Q3=L3+(34N−F3fQ3)C =49.5+(45−3216)10 =49.5+8.125 =57.625
Step 4:
The table below shows the marks obtained by a group of Form 4 students in school mathematics test.

Estimate the interquartile range.
Solution:
Upper quartile, Q3 = the 34(60)th observation
= the 45thobservation
Step 2:
Lower quartile, Q1=L1+(14N−F1fQ1)C =39.5+(15−1220)10 =39.5+1.5 =41
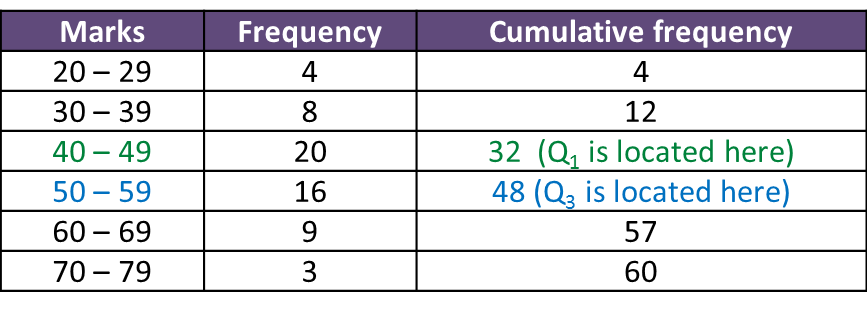
Method 1: From Cumulative Frequency Table
Step 1:
Lower quartile, Q1 = the
14(60)th
observation
= the 15thobservation
Upper quartile, Q3 = the 34(60)th observation
= the 45thobservation

Step 2:
Step 3:
Step 4:
Interquartile Range
= upper quartile – lower quartile
= Q3– Q1
= 57.625 – 41
= 16.625