9.1 Longitudes
1. A great circle is a circle with the centre of the Earth as its centre.
2. A meridian is half of a great circle from the North pole to the South pole.
3. The longitude of the Greenwich Meridian is 0o.
4. The longitude of a meridian is determined by:
(a) The angle between the meridian plane and the Greenwich Meridian.
(b) The position of the meridian to the east or west of the Greenwich Meridian.
Example:
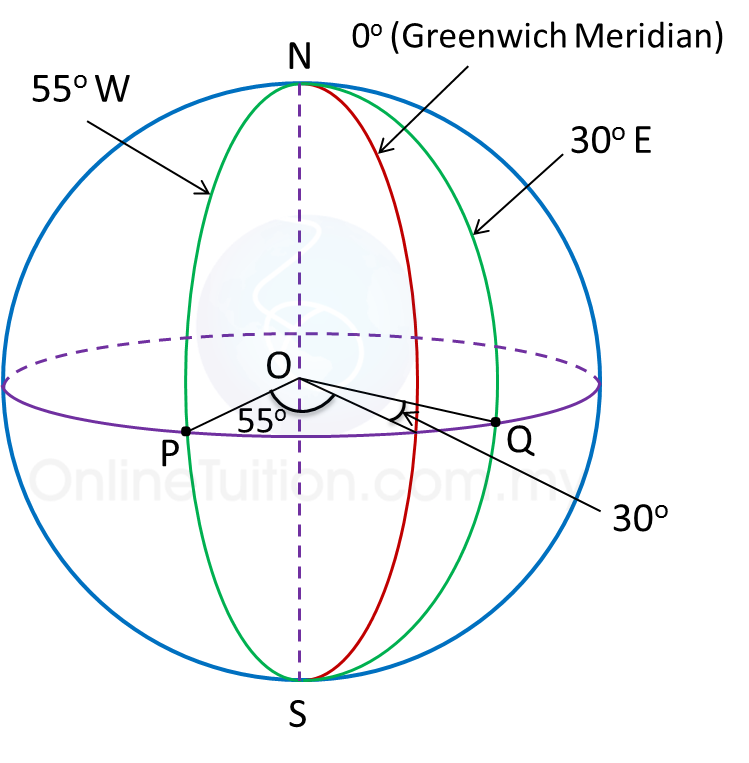
Longitude of P is 55o W.
Longitude of Q is 30o E.
5. All points on the same meridian have the same longitude.
Difference between Two Longitudes
1. If both the meridians are on the east (or west) of the Greenwich Meridian, subtract the angles of the longitudes.
2. If both the meridians are on the opposite sides of the Greenwich Meridian, add the angles of the longitudes.