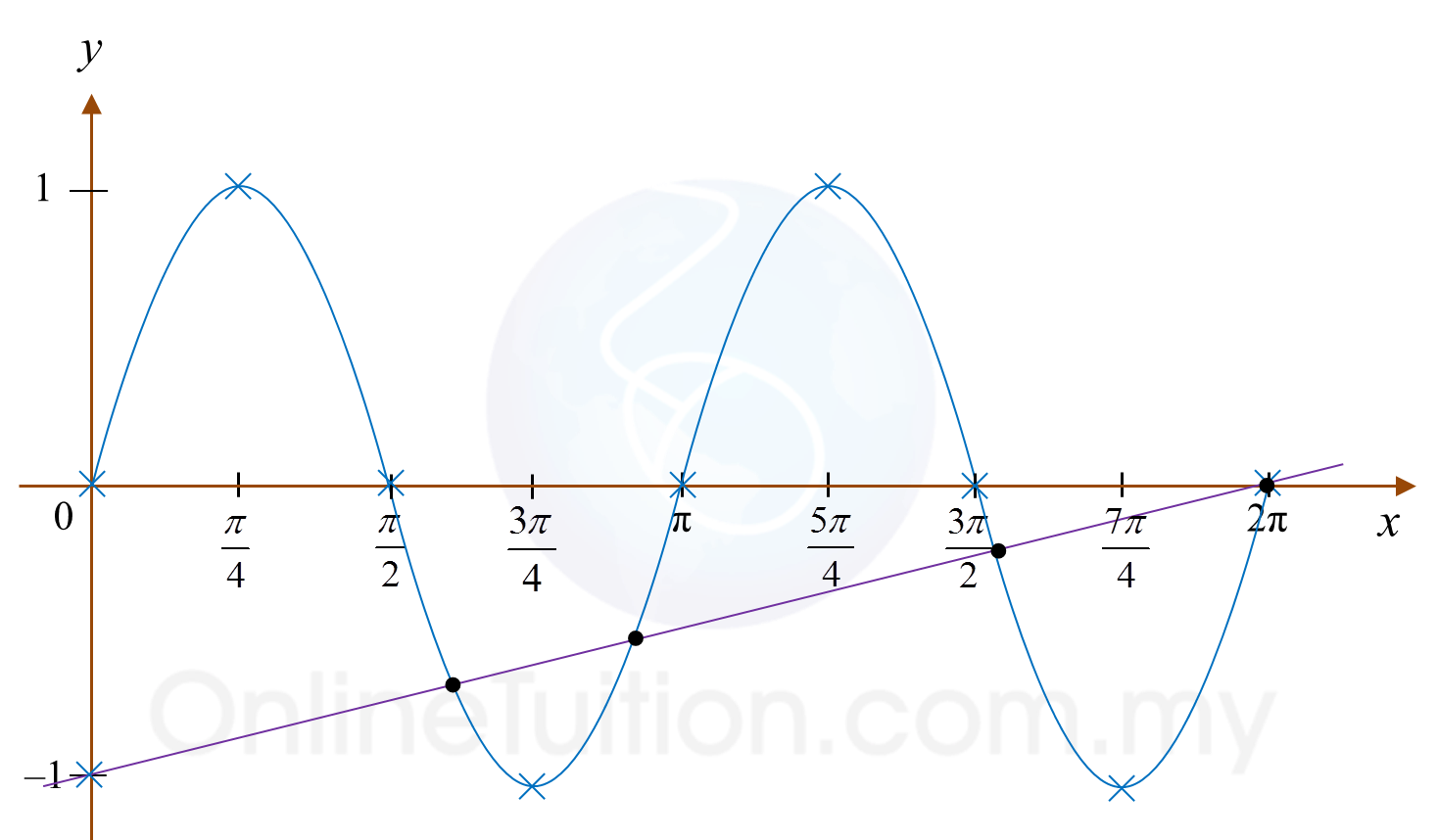
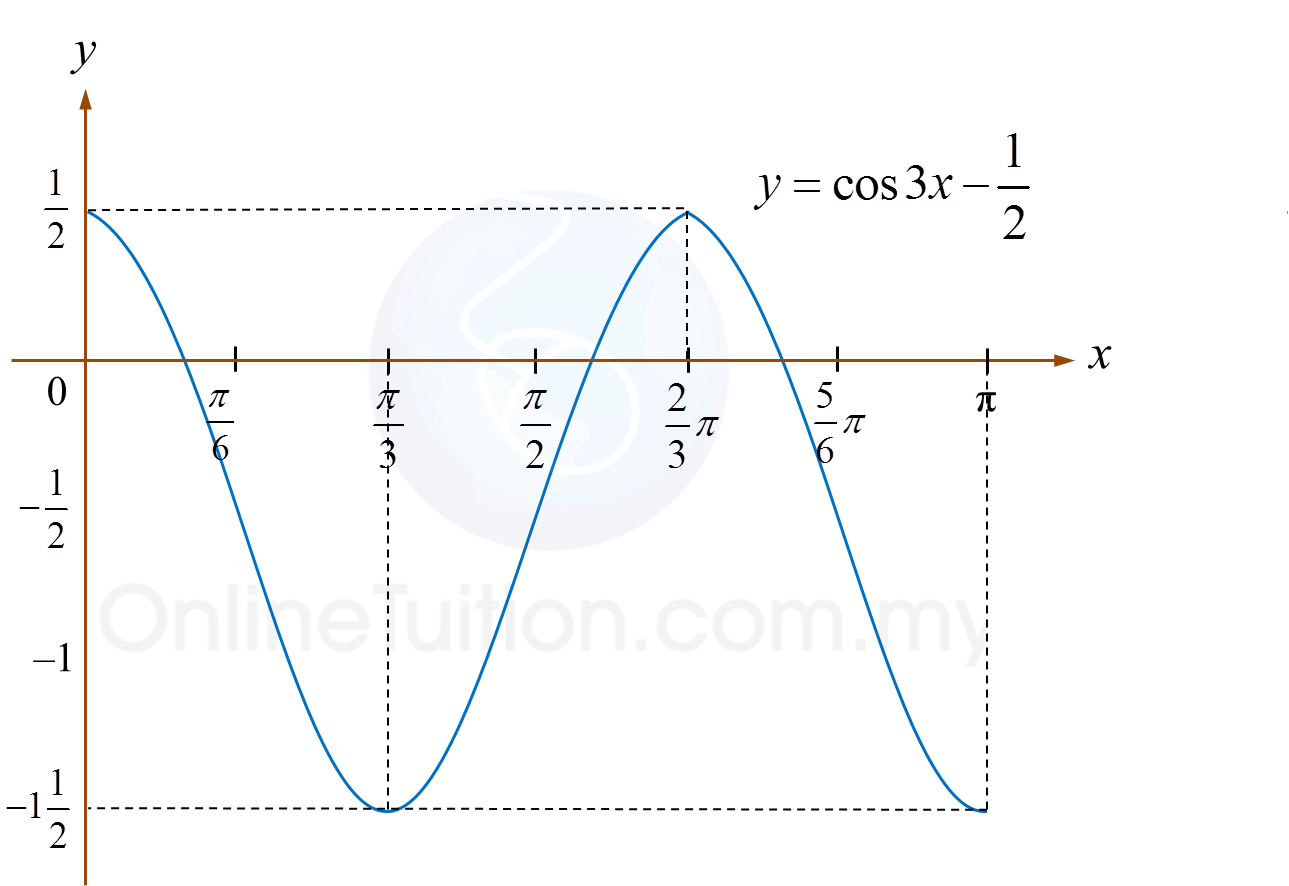
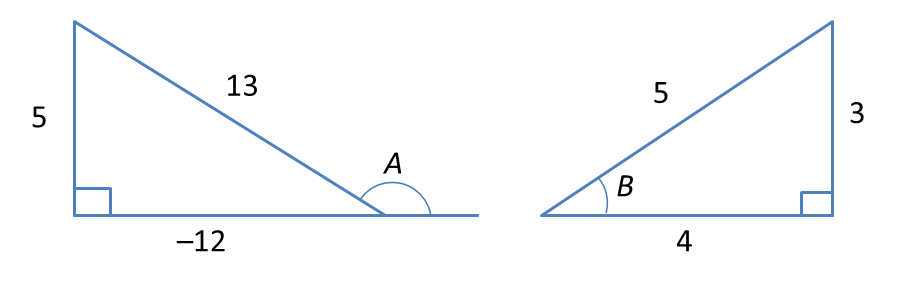
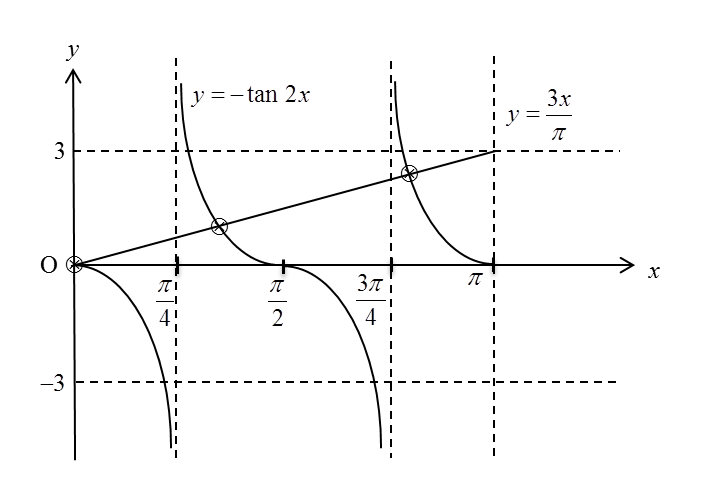Question 4:
Find all the angles between 0° and 360° which satisfy the following equations:
(a) 2 sin ( 2x – 50o) = –1
(b) 15 sin2x = sin x + 4 sin 30o
(c) 7 sin x cos x = 1
Solution:
(a)
2 sin ( 2x – 50o) = –1
sin ( 2x – 50o) = – ½
basic angle ( 2x – 50o) = –30o ← (sin is negative at third and fourth quadrants)
2x – 50o = –30o, 180o + 30o, 360o – 30o, 360o + 180o+ 30o
← (Take the angles in the range of 0o ≤ x ≤ 720o, which in 2 complete revolutions)
2x – 50o = –30o, 210o, 330o, 570o
2x = 20o, 260o, 380o, 620o
x = 10o, 130o , 190o, 310o
(b)
15 sin2x = sin x + 4 sin 30o
15 sin2x = sin x + 4 (½) ← (sin 30o = ½)
15 sin2x = sin x + 2
15 sin2x – sin x – 2 = 0
(5 sin x – 2)(3 sin x + 1) = 0
sin x =
25
or sin x = – ⅓
When sin x =
25
Basic angle x = 23º 35’
x = 23º 35’, 180º – 23º 35’
x = 23º 35’, 156º 25’
When sin x = – ⅓ ← (sin is negative at third and fourth quadrants)
Basic angle x = 19º 28’
x = 180º + 19º 28’, 360º – 19º 28’
x = 199º 28’, 340º 32’
Hence x = 23º 35’, 156º 25’, 199º 28’, 340º 32’.
(c)
7 sin x cos x = 1
sin x cos x =
17
2 sin x cos x =
27
← ( × 2 for both sides)
sin 2x =
27
sin 2x = 0.2857
Basic angle x = 16º 36’
2x = 16º 36’, 180º – 16º 36’, 360º + 16º 36’, 360º + 180º – 16º 36’
2x = 16º 36’, 163º 24’, 376º 36’, 523º 24’
x = 8º 18’, 81º 42’, 188º 18’, 261º 42’
Hence x = 8º 18’, 81º 42’, 188º 18’, 261º 42’.
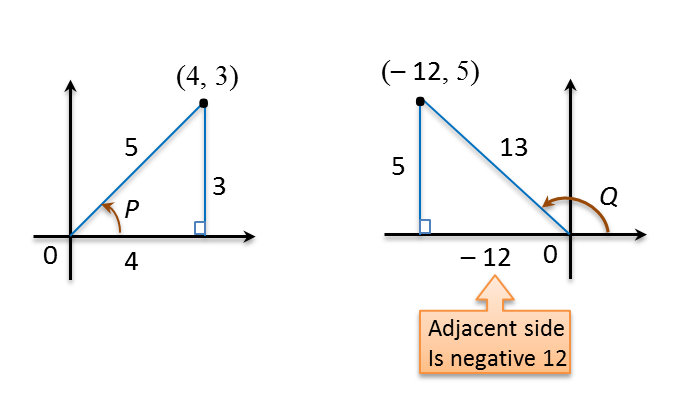 sinP=35,cosP=45sinQ=513,cosQ=−1213cos(P+Q)=cosAcosB−sinAsinB=(45)(−1213)−(35)(513)=−4865−1565=−6365
sinP=35,cosP=45sinQ=513,cosQ=−1213cos(P+Q)=cosAcosB−sinAsinB=(45)(−1213)−(35)(513)=−4865−1565=−6365