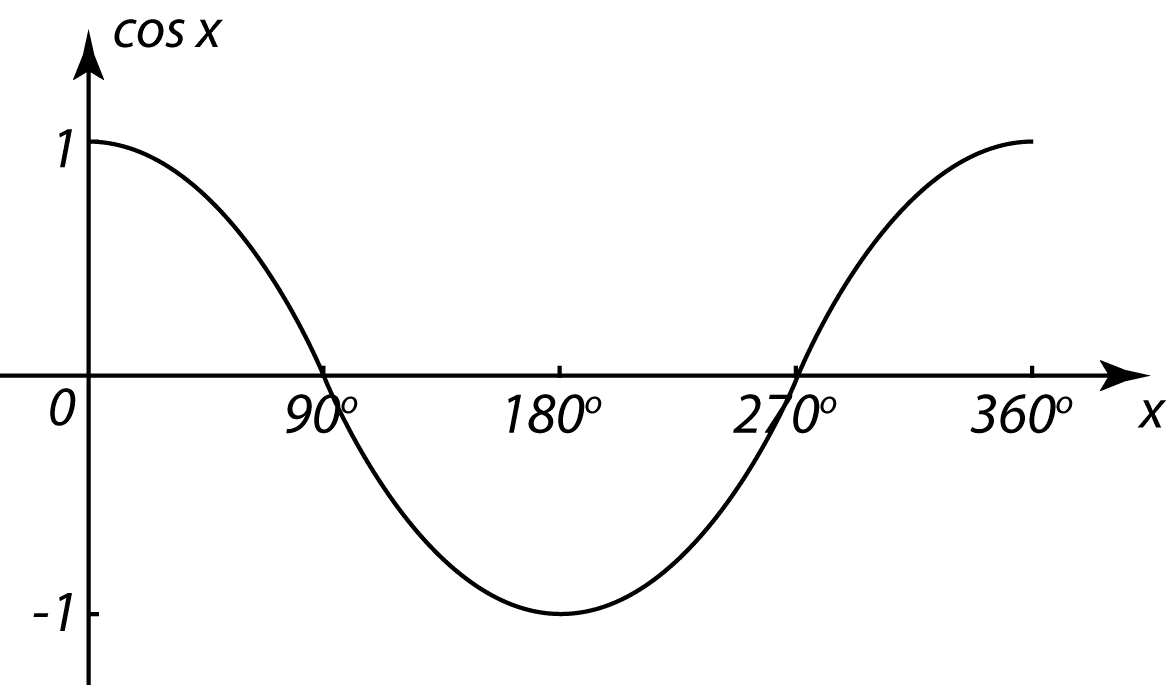
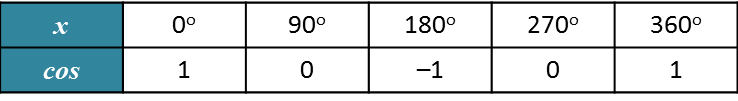
5.4 Basic Trigonometric Identities
Three
basic trigonometric identities are:
[adinserter block="3"]
Example 1 (To Prove Trigonometric Identities which involve the Three Basic Identities)
Prove each of the following trigonometric identities.
(a) sin2 x – cos2 x = 1 – 2 cos2 x
(b) (1 – cosec2 x) (1– sec2 x) = 1
Solution:
(a)
sin2 x– cos2 x = 1 – 2 cos2x
LHS: sin2 x – cos2 x
= 1 – cos2 x – cos2 x
= 1 – 2 cos2 x (RHS)
(b)
(1−cosec2x)(1−sec2x)=1LHS:(1−cosec2x)(1−sec2x)=(−cot2x)(−tan2x)=(cot2x)(tan2x)=(1tan2x)tan2x=1(RHS)
Example 2 (To Solve Trigonometric Equations which involve the Three Basic Identities)
Solve the following trigonometric equations for 0o≤ x ≤ 360o.
(a) sin2 x cos x + 1 = cos x
(b) 2 cosec2 x – 5 cot x = 0
Solution:
(a)
sin2 x cos x + 1 = cos x
(1 – cos2 x) cos x + 1 = cos x
cos x – cos3 x + 1 = cos x
cos3 x = 1
cos x = 1
x = 0o, 360o
(b)
2 cosec2 x – 5 cot x = 0
2 (1 + cot2 x) – 5 cot x = 0
2 + 2 cot2 x – 5 cot x = 0
2 cot2 x – 5 cot x + 2 = 0
(2 cot x – 1) (cot x – 2) = 0
cot x= ½ or cotx = 2
cot x= ½ or cot x = 2
tan x = 2 tan x = ½
x =63.43o, 243.43o x = 26.57o, 206.57o
(Note: tangent is positive in the first and third quadrants)
Thus, x = 26.57o, 63.43o, 206.57o, 243.43o