[adinserter block="3"]
Question 1:
R, S and T in Figure below show three types of interactions between organisms.
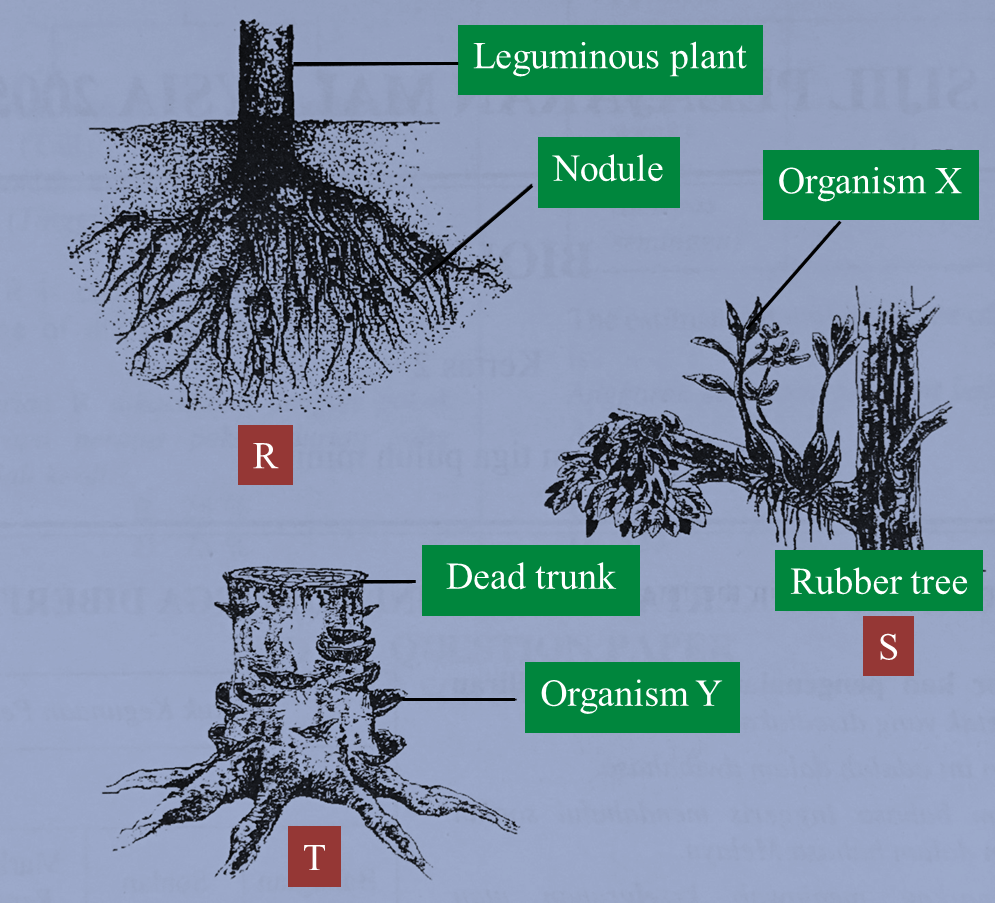
(a)(i) Name the type of interaction represented by R and S.
(ii) Describe the interaction represented by R.
[adinserter block="3"]
(b)(i) In the interactions represented by S and T, what terms are used to describe organisms X and Y?
(ii) State one characteristics of organism X that adapts it for the interaction.
(c) The rubber tree in the interaction represented by S dies.
Explain what will happen to organism X.
(d) Saw dust can be used in the interaction represented by T for the commercial cultivation of mushrooms.
Explain how mushrooms can grow on saw dust.
[adinserter block="3"]
Answer:
(a)(i)
Organism R: Mutualism/ symbiosis
Organism S: Commensalism
(a)(ii)
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the root nodules fix nitrogen to form ammonia which is used by the plant while Rhizobium bacteria get shelter from the plant.
[adinserter block="3"]
(b)(i)
X: Epiphyte
Y: Saprophyte
(b)(ii)
The presence of aerial roots which absorb moisture from the air
(c)
X continues to grow because it photosynthesises.
(d)
Mushrooms grow on dead organic matter.
Mushrooms secrete enzymes which digest the complex organic matter to simple substances.
[adinserter block="3"]
R, S and T in Figure below show three types of interactions between organisms.

(a)(i) Name the type of interaction represented by R and S.
(ii) Describe the interaction represented by R.
[adinserter block="3"]
(b)(i) In the interactions represented by S and T, what terms are used to describe organisms X and Y?
(ii) State one characteristics of organism X that adapts it for the interaction.
(c) The rubber tree in the interaction represented by S dies.
Explain what will happen to organism X.
(d) Saw dust can be used in the interaction represented by T for the commercial cultivation of mushrooms.
Explain how mushrooms can grow on saw dust.
[adinserter block="3"]
Answer:
(a)(i)
Organism R: Mutualism/ symbiosis
Organism S: Commensalism
(a)(ii)
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the root nodules fix nitrogen to form ammonia which is used by the plant while Rhizobium bacteria get shelter from the plant.
[adinserter block="3"]
(b)(i)
X: Epiphyte
Y: Saprophyte
(b)(ii)
The presence of aerial roots which absorb moisture from the air
(c)
X continues to grow because it photosynthesises.
(d)
Mushrooms grow on dead organic matter.
Mushrooms secrete enzymes which digest the complex organic matter to simple substances.
[adinserter block="3"]






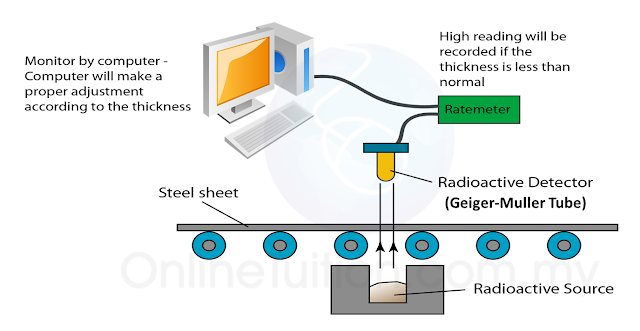
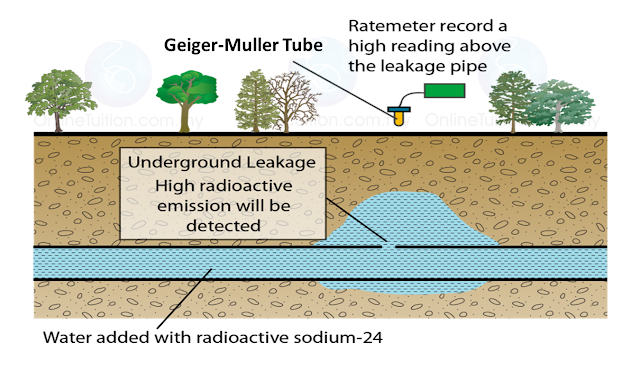

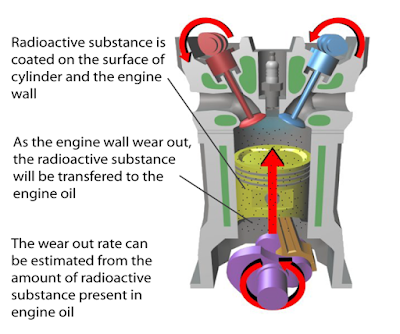

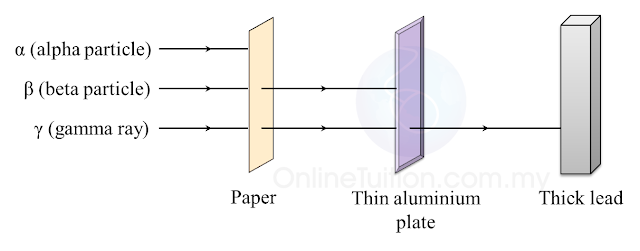
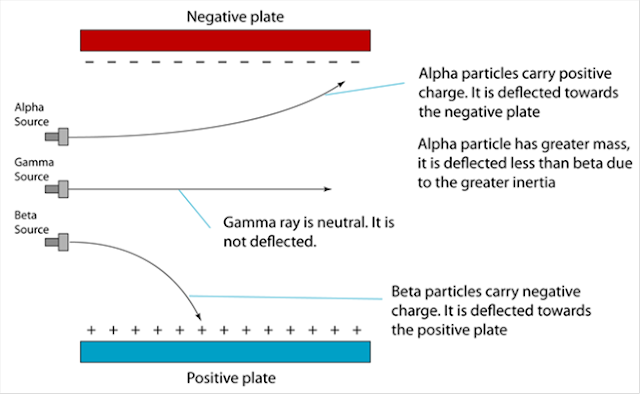

 (a) Name the process in Diagram 1. [1 mark]
(a) Name the process in Diagram 1. [1 mark]


