Question 1:
(a)(i) Diagram below shows an electron micrograph of cellular components of human blood.
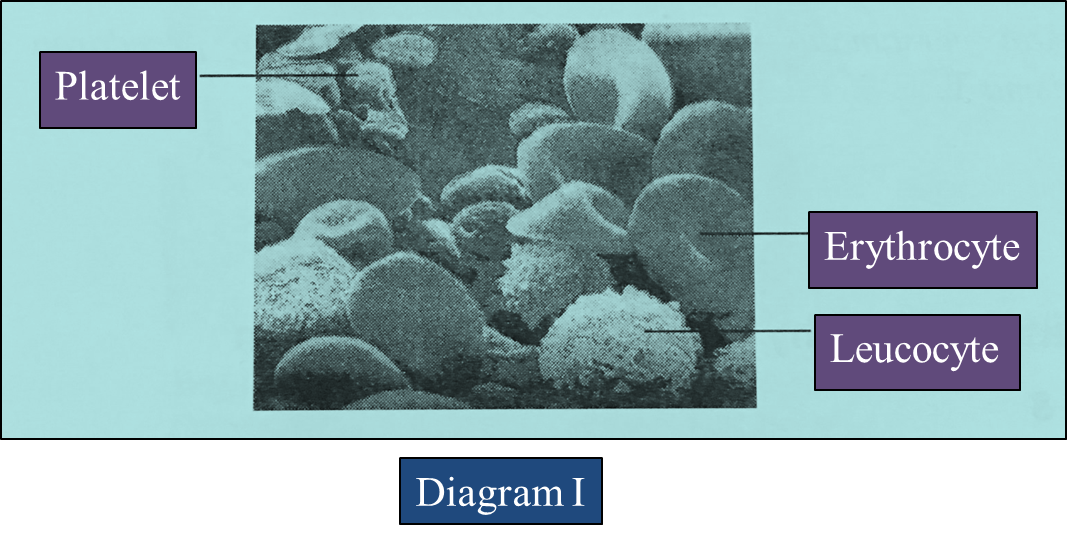
Based on Diagram I, explain how platelets help to stop bleeding when a wound occurs. [4 marks]
(ii) A blood test shows that a man’s erythrocytes count is below normal.
Explain the possible consequences of this condition on his health.
What type of food should be included in his diet to improve this condition? [8 marks]
(b) Diagram II shows the blood circulatory system in organism P and organism Q.
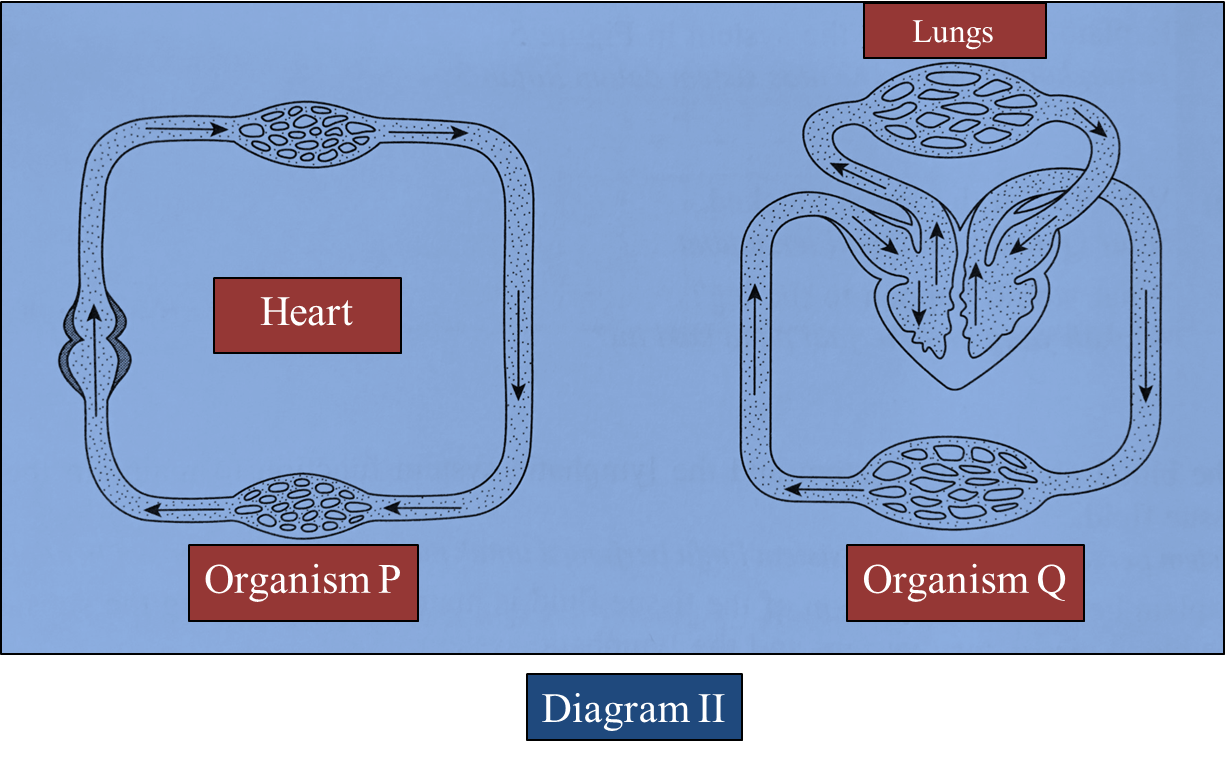
Based on Diagram II:
(i) Give one example of organism P and organism Q. [2 marks]
(ii) Describe the similarities and differences between the blood circulatory system in organism P and organism Q. [6 marks]
Answer:
(a)(i) Diagram below shows an electron micrograph of cellular components of human blood.

Based on Diagram I, explain how platelets help to stop bleeding when a wound occurs. [4 marks]
(ii) A blood test shows that a man’s erythrocytes count is below normal.
Explain the possible consequences of this condition on his health.
What type of food should be included in his diet to improve this condition? [8 marks]
(b) Diagram II shows the blood circulatory system in organism P and organism Q.

Based on Diagram II:
(i) Give one example of organism P and organism Q. [2 marks]
(ii) Describe the similarities and differences between the blood circulatory system in organism P and organism Q. [6 marks]
Answer:
(a)(i)
- Platelets clump together and produce thrombokinase.
- Thrombokinase converts prothrombin to thrombin.
- Thrombin converts fibrinogen (a type of soluble protein plasma) to fibrin (vitamin K is needed in the formation of prothrombin).
- Fibrin forms a network to trap the erythrocytes
- To form a clot
(a)(ii)
- Less red blood cells to combine with oxygen
- Less oxygen is transported to the body cells.
- Less energy is produced
- Resulting in tiredness/ pale looking appearance/ anaemia
- Need food which is rich in iron
- Examples: Cockles, liver, spinach
(b)(i)
P: Fish
Q: Human being
(b)(ii)
Similarities:
- Both have a closed circulation
- Blood flows in blood vessels