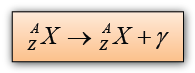Alpha Decay
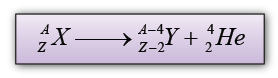
- During an alpha decay, a radioactive atom X decay and emits an alpha particle (H42e ).
- Atom X losses 2 neutron and 2 proton and become atom Y.
Example
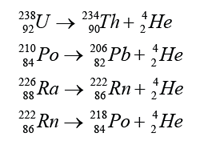
Beta decay
- A beta particles is an electron emitted from a nucleus.
- The beta particles are very small and move with very high speed.
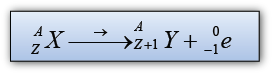
- During a beta decay, a radioactive atom X decay and emits a beta particle (e0−1 ).
- One of the neutron is disintegrated to become proton and electron. The electron is emitted out from the nucleus whereas the proton stay in the nucleus.
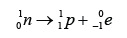
- Therefore proton number increase by 1 and the nucleon number remain unchanged.
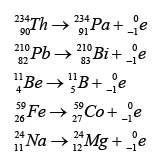
Gamma Emission
Gamma emission causes no change in nucleon number or proton number.