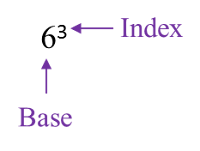
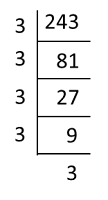
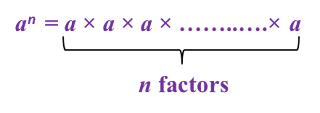Question 13:
Solution:
Solution:
Question 14:
Solution:
Solution:
Question 15:
Solution:
Solution:
Question 16:
Solution:
Solution:
Question 17:
Find the value of the following.
(a) (23)2 × 24 ÷ 25
(b)
Solution:
(a)
(23)2 × 24 ÷ 25= 26 × 24 ÷ 25
= 26+4-5
= 25
= 32
(b)