7.2 Probability of the Combination of Two Events
1. For two events, A and B, in a sample space S, the events A ∩ B (A and B) and A υ B (A or B) are known as combined events.
2. The probability of the union of sets A and B is given by:
3. The probability of the union of sets A and B can also be calculated using an alternative method, i.e.
4. The probability of event A and event B occurring, P(A ∩ B) can be determined by the following formula.
Example:
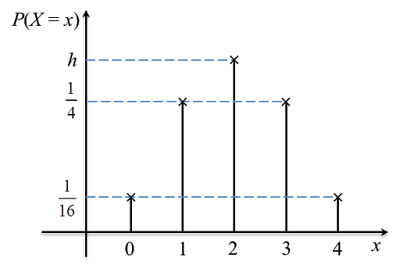
Given a universal set ξ = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15}. A number is chosen at random from the set ξ . Find the probability that
(a) an even number is chosen.
(b) an odd number or a prime number is chosen.
Solution:
The sample space, S = ξ
n(S) = 14
(a)
Let A = Event of an even number is chosen
A = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14}
n (A) = 7
(b)
Let,
B = Event of an odd number is chosen
C = Event of a prime number is chosen
B = {3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15} and n (B) = 7
C = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13} and n (C) = 6
The event when an odd number or a prime number is chosen is B υ C.
P (B υ C) = P (B) + P (C) – P (B ∩ C)
B ∩ C = {3, 5, 7, 11, 13}, n (B ∩ C) = 5