Question 5:
The diameter of oranges harvested from a fruit orchard has a normal distribution with a mean of 3.2 cm and a variance of 2.25 cm.
Calculate
(a) the probability that an orange chosen at random from this fruit orchard has a diameter of more than 3.8 cm.
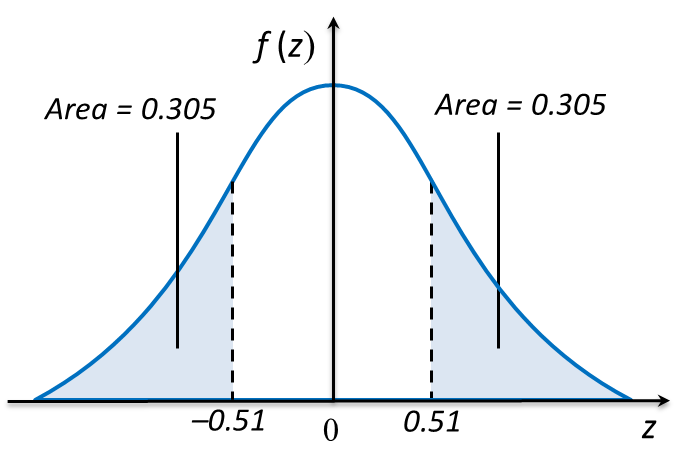
(b) the value of k if 30.5 % of the oranges have diameter less than k cm.
Solution:
µ = 3.2 cm
σ2 = 2.25cm
σ = √2.25 = 1.5 cm
Let X represents the diameter of an orange.
X ~ N (3.2, 1.52)
(a)
(b)