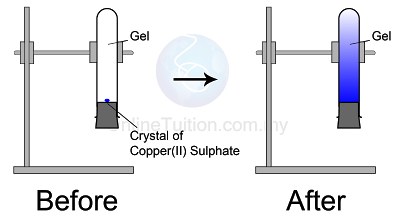
Matter exists in 3 states of matter, namely, solid state, liquid state and gaseous state.
Characteristics of Matter in Solid, Liquid and Gaseous State
| Characteristics | Solid |
Liquid |
Gas |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Arrangement of Particles | Particles are arranged in orderly manner and close to one another. |
Particles are not arranged in order. The space between particles is moderately large. |
The particles are very far apart and randomly arrange. |
| Movement of Particles | Particles vibrate at fixed positions. | Particles move randomly and slowly and sometimes will collide against each other. | The particles move randomly in all directions at great speed. |
| Force of Attraction between particles | very strong | Strong but weaker than in the solid state. | very weak |
| Ability to be compressed | Very difficult to be compressed because the particles are packed closely. | Not easily compressed because the particles are packed quite closely. | Easily compressed because the particles are very far apart. |
| Volume | Fixed | Fixed | Follows the container |
| Heat Energy content | Lowest Energy Content | Moderate energy content. | Highest energy content |
| Shape | Fixed | Follows the container | Fills the whole container |