- Carbohydrate consist of the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
- The H : O ratio in all carbohydrate molecules is 2 : 1.
- Examples of carbohydrate include starch, sugar, glycogen and cellulose.
- Excess carbohydrates are stored in the form of glycogen in the liver. Some are converted to fat and stored in the adipose tissues below the skin and around organs.
- There are three types of carbohydrates:
- Monosaccharides
- Disaccharides
- Polysaccharides
3.8.1 Cell Division (Structured Questions)
Question 1:
Diagram 1 shows the stages of cell division.

(a)(i) Name the type of cell division as shown in Diagram 1. [1 mark]
(ii) Give reason to your answer in (a)(i). [1 mark]
(b) Arrange the stages of cell division P, Q, R and S in a correct sequence in the boxes given. [1 mark]

(c)(i) Name structure W. [1 mark]
(ii) How many structures W in each cell at stage P? [1 mark]
(d) What happens to structure W if exposed to radioactive radiation? [1 mark]
Answer:
(a)(i) Mitosis
(a)(ii) The daughter cells contain the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
(b)

(c)(i) Chromosome
(c)(ii) 46
(d) Mutation may occur
Diagram 1 shows the stages of cell division.

(a)(i) Name the type of cell division as shown in Diagram 1. [1 mark]
(ii) Give reason to your answer in (a)(i). [1 mark]
(b) Arrange the stages of cell division P, Q, R and S in a correct sequence in the boxes given. [1 mark]

(c)(i) Name structure W. [1 mark]
(ii) How many structures W in each cell at stage P? [1 mark]
(d) What happens to structure W if exposed to radioactive radiation? [1 mark]
Answer:
(a)(i) Mitosis
(a)(ii) The daughter cells contain the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
(b)

(c)(i) Chromosome
(c)(ii) 46
(d) Mutation may occur
Question 2:
Diagram 2 shows a process of cell division. Chromosomes at stage B are not shown.

(a)(i) Name the process shown in Diagram 2. [1 mark]
(ii) State the importance of the process in (a)(i). [1 mark]
(b)(i) During stage C, the chromosomes line up on the equator.
What happens to the chromosomes during this stage? [1 mark]
(ii) What is the effect of the process in (b)(i) on the offspring? [1 mark]
(c) In Diagram 2, draw the chromosome at stage B. [1 mark]
(d) How many daughter cells are produced at the end of Division II in Diagram 1? [1 mark]
Answer:
(a)(i) Meiosis
(a)(ii) Production of gametes
(b)(i) Crossing-over
(b)(ii) Variations
(c)

(d) 4 daughter cells are produced
Diagram 2 shows a process of cell division. Chromosomes at stage B are not shown.

(a)(i) Name the process shown in Diagram 2. [1 mark]
(ii) State the importance of the process in (a)(i). [1 mark]
(b)(i) During stage C, the chromosomes line up on the equator.
What happens to the chromosomes during this stage? [1 mark]
(ii) What is the effect of the process in (b)(i) on the offspring? [1 mark]
(c) In Diagram 2, draw the chromosome at stage B. [1 mark]
(d) How many daughter cells are produced at the end of Division II in Diagram 1? [1 mark]
Answer:
(a)(i) Meiosis
(a)(ii) Production of gametes
(b)(i) Crossing-over
(b)(ii) Variations
(c)

(d) 4 daughter cells are produced
4.1 Chemical Composition of the Cell
- The elements found in the cell include
- carbon,
- oxygen,
- hydrogen,
- nitrogen,
- sulphur,
- phosphorus,
- calcium,
- sodium,
- potassium,
- magnesium,
- iron
- chlorine,
- The chemical compounds in the cell can be classified into two groups,
- organic: compounds which contain the element carbon and originate from living things. Example: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids
- inorganic: compounds which do not originate from living things. Example: water and mineral salts.
- .Organic compounds are synthesised by the cells themselves whereas inorganic compounds are not synthesised by the cells themselves but are obtained from the external environment.
3.5.2 The Movement of Substances across the Plasma Membrane in Everyday Life (Objective Questions)
[adinserter block="3"]
[WpProQuiz 2]
[adinserter block="3"]
[WpProQuiz 2]
[adinserter block="3"]
3.5.1 The Movement of Substances across the Plasma Membrane (Objective Questions)
[adinserter block="3"]
[WpProQuiz 1]
[adinserter block="3"]
[WpProQuiz 1]
[adinserter block="3"]
3.4.2 The Movement of Substances Across the Plasma Membrane in Everyday Life (Structured Question 1 & 2)
Question 1:
Diagram I and Diagram II show the movement of substances P and Q across the plasma membrane respectively. The movement of P needs energy but the movement of Q does not.
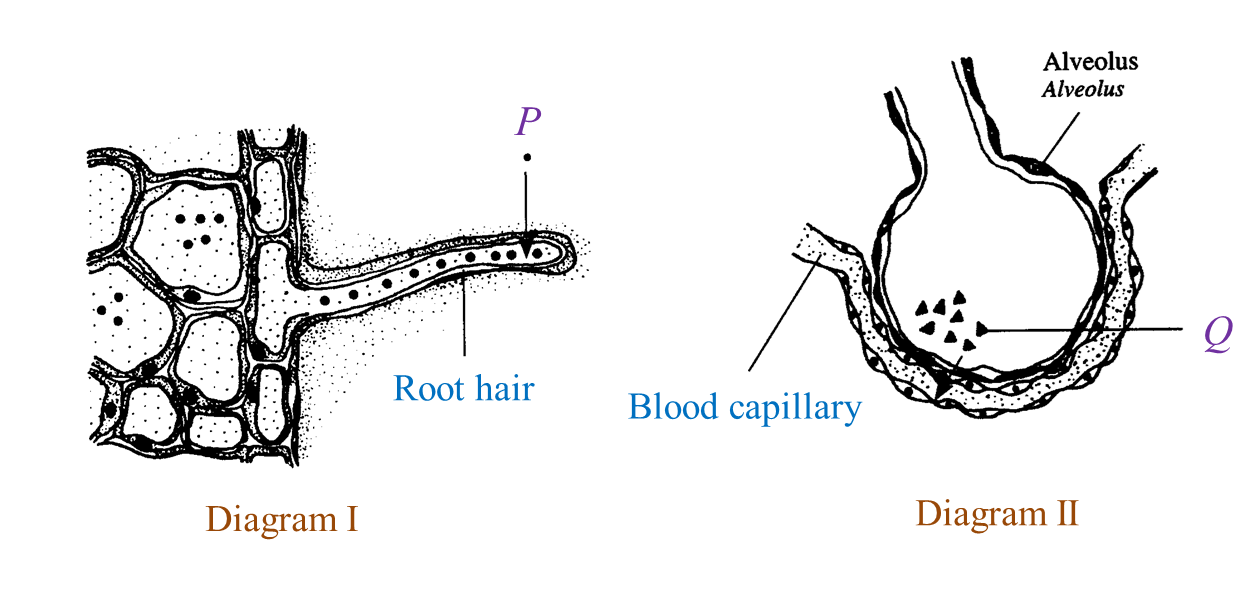 (a) Name the processes involved in the movement of P and Q. (2 marks)
(a) Name the processes involved in the movement of P and Q. (2 marks)(b)(i) Name one example of P and Q. (2 marks)
(b)(ii) Describe the movement of Q shown in Diagram II. (2 marks)
(c) Diagram III shows the condition of a plant cell before and after being immersed in a type of solution. (3 marks)
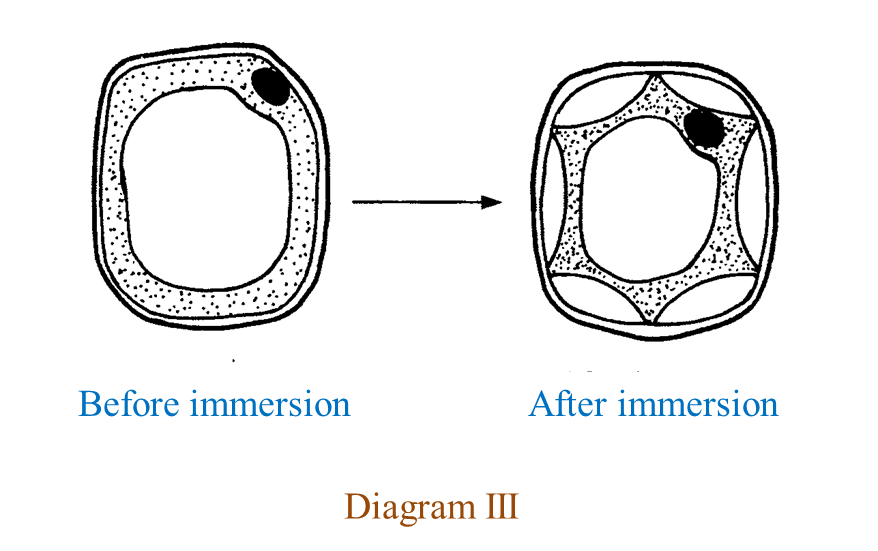
Explain the condition of the cell after being immersed in the solution.
(d) A housewife makes mango pickles by immersing mango slices in a concentrated sugar solution.
State one advantage and two disadvantages of the method used, compared to storing fresh mangoes. (3 marks)
Answer:
(a)
P: Active transport
Q: Simple diffusion
(b)(i)
P: Nitrate
Q: Oxygen
(b)(ii)
The partial pressure of Q is higher in the alveolus than in the blood capillary. As a result, Q diffuses into the blood capillary following the concentration gradient.
(c)
The plasma membrane is pulled away from the cell wall, the vacuole becomes small, as a result the cell becomes flaccid and plasmolysis occurs.
(d)
Advantage: It keeps food for longer period.
Disadvantages:
1. The sugar content of the food is too high.
2. Some of the nutrients such as vitamin C are lost.
Question 2:
Diagram I below shows a plant cell that has been immersed in 30% sucrose solution.
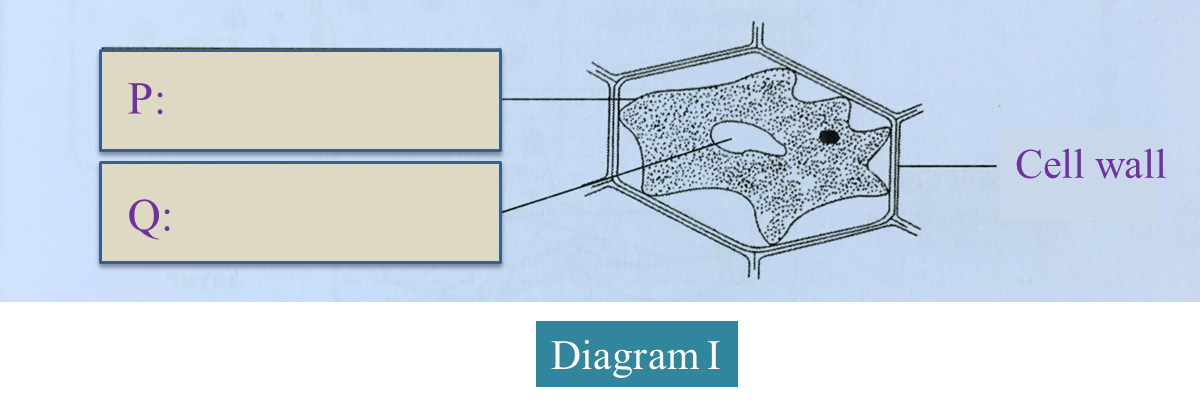
(a)(i) On the diagram, label P and Q. (2 marks)
(a)(ii) Name the solution which filled the space between the cell wall and P.
Explain how the solution filled the space. (2 marks)
(b) The plant cell in the Diagram has undergone plasmolysis.
Explain how this happened. (2 marks)
(c) Diagram II and III below show the condition of two plants which are added with fertilizer. The plant in Diagram III is added with excess fertilizer.
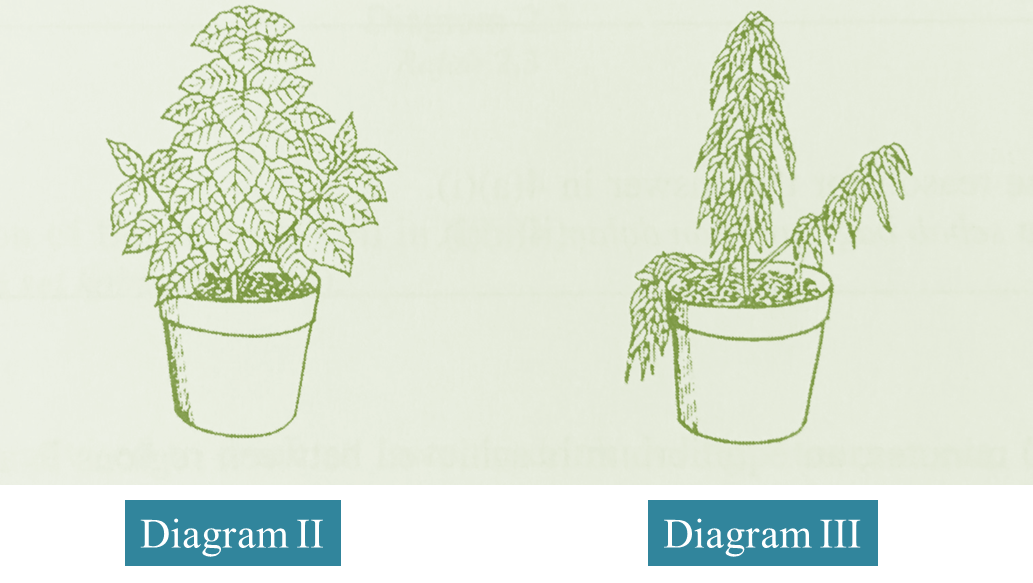
Explain the condition of the plant in Diagram III. (3 marks)
(d) Diagram IV shows a method of preserving vegetables.
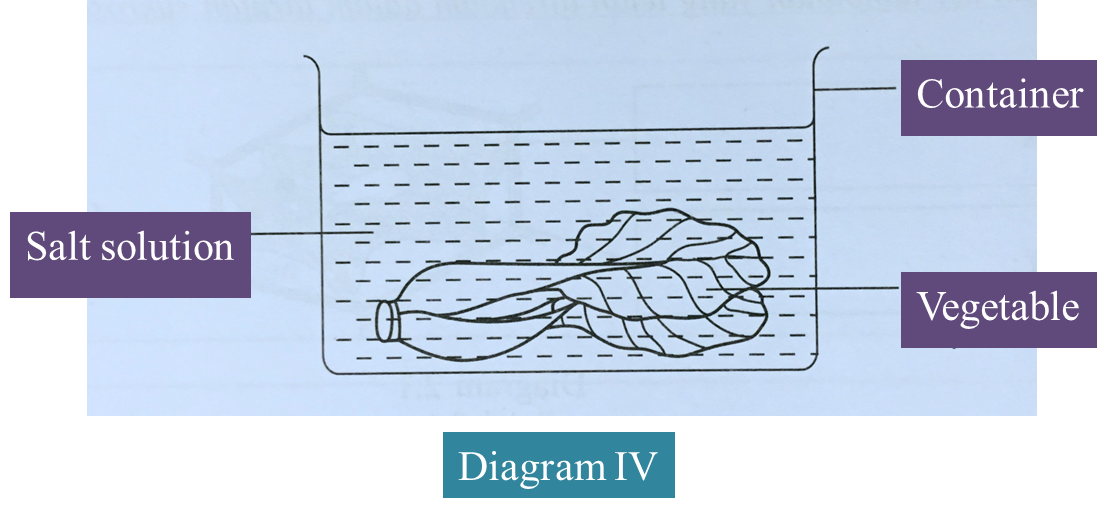
Explain the method used. (3 marks)
Answer:
(a)(i)
P – Plasma membrane
Q – Vacuole
(a)(ii)
Solution: Sucrose solution
Explanation: Cell wall is permeable to allow sucrose solution to pass through and fill up the spaces.
(b)
When water molecules diffuse out of the large vacuole by osmosis, the plasma membrane will be pulled away from the cell wall. The cytoplasm shrinks due to osmosis.
(c)
Excess fertilizer will cause the soil water to be hypertonic towards the root hair cells. As a result, water from the root hair cells diffuses out to the soil by osmosis. The cells become plasmolysed and this leads to wilting.
(d)
Salting – Concentrated salt solution is used to soak vegetables, The hypertonic solution causes vegetable tissues to be dehydrated. Microorganisms lose water by osmosis and cannot live without water.
Diagram I below shows a plant cell that has been immersed in 30% sucrose solution.

(a)(i) On the diagram, label P and Q. (2 marks)
(a)(ii) Name the solution which filled the space between the cell wall and P.
Explain how the solution filled the space. (2 marks)
(b) The plant cell in the Diagram has undergone plasmolysis.
Explain how this happened. (2 marks)
(c) Diagram II and III below show the condition of two plants which are added with fertilizer. The plant in Diagram III is added with excess fertilizer.

Explain the condition of the plant in Diagram III. (3 marks)
(d) Diagram IV shows a method of preserving vegetables.

Explain the method used. (3 marks)
Answer:
(a)(i)
P – Plasma membrane
Q – Vacuole
(a)(ii)
Solution: Sucrose solution
Explanation: Cell wall is permeable to allow sucrose solution to pass through and fill up the spaces.
(b)
When water molecules diffuse out of the large vacuole by osmosis, the plasma membrane will be pulled away from the cell wall. The cytoplasm shrinks due to osmosis.
(c)
Excess fertilizer will cause the soil water to be hypertonic towards the root hair cells. As a result, water from the root hair cells diffuses out to the soil by osmosis. The cells become plasmolysed and this leads to wilting.
(d)
Salting – Concentrated salt solution is used to soak vegetables, The hypertonic solution causes vegetable tissues to be dehydrated. Microorganisms lose water by osmosis and cannot live without water.
3.4.1 The Movement of Substances Across the Plasma Membrane (Structured Question 1 & 2)
Question 1:
Diagram I and Diagram II show two different types of movement of substances across the plasma membrane.
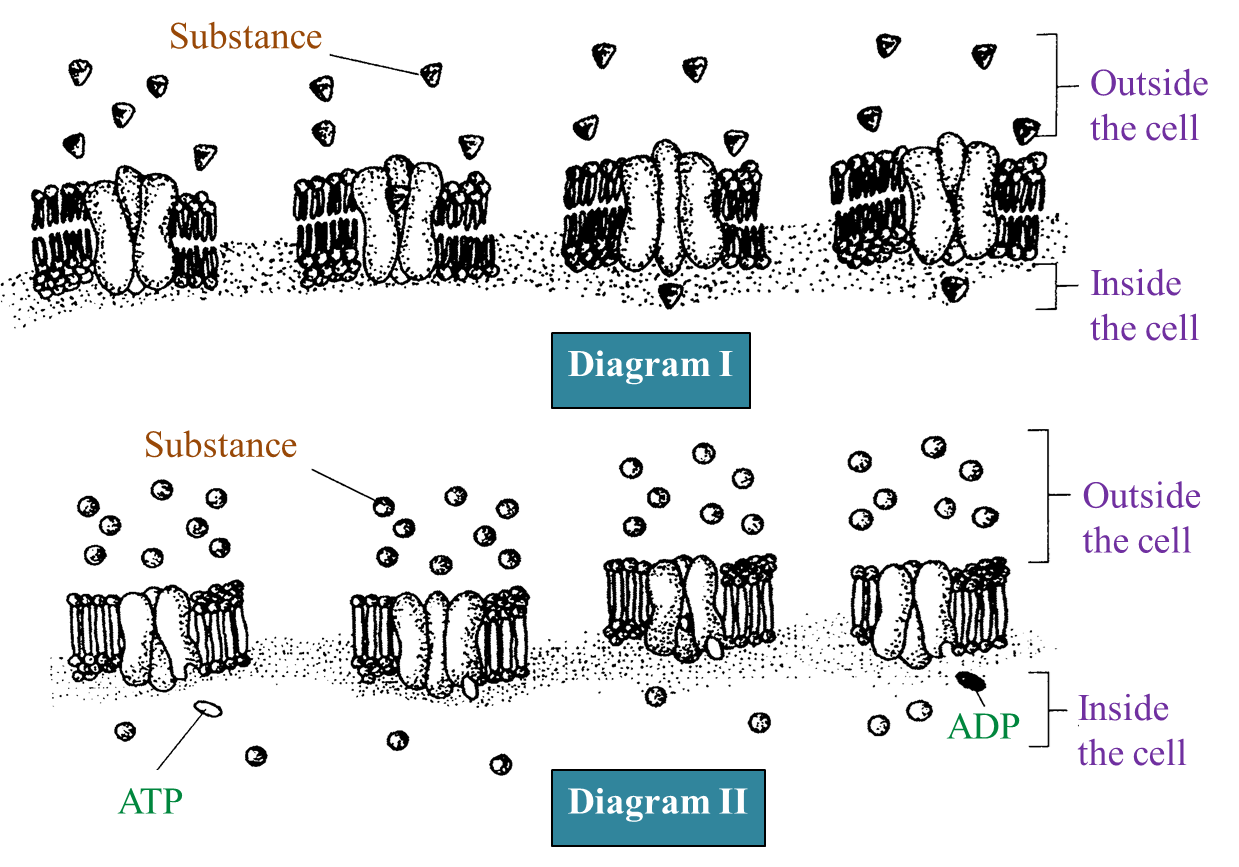
(a) In Diagram I. label the following structures:
Answer:
(a)
Diagram I and Diagram II show two different types of movement of substances across the plasma membrane.

(a) In Diagram I. label the following structures:
- Phospholipid bilayer, with letter R
- Carrier protein, with letter S [2 marks]
(b) State two characteristics of the phospholipid bilayer. [2 marks]
(c) Name the process of the movement of substances across the plasma membrane as shown in Diagram I and Diagram II. [2 marks]
(d)(i) Glucose molecules are transported across the plasma membrane into the cell through the process shown in Diagram I. Explain why. [2 marks]
(ii) If the substances in Diagram II are calcium ions, describe how they are transported into the cell. [4 marks]
Answer:
(a)

(b)
- It consists of hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails
- The hydrophilic heads are facing the exterior and the interior of the cell
- The bilayer is dynamic/ not static
(Choose any 2)
(c)
Process in Diagram I – Facilitated diffusion
Process in Diagram II – Active transport
(d)(i)
- Glucose consists of uncharged large sized molecules which cannot pass through the phospholipid bilayer.
- It needs a specific carrier protein to transport it across the phospholipid bilayer.
(d)(ii)
- By active transport – The movement of calcium ions is against the concentration gradient
- And it needs energy which is produced by cellular respiration ( in the form of ATP molecules)
- Carrier proteins bind with the calcium ions and change their shape, thus carrying the ions across the plasma membrane.
3.2.3 Types of Solution – Hypertonic
What is Hypertonic Solution?
Hypertonic solution is the solution that has lower water potential than the other solution.Water Concentration and Solute Concentration of a Cell in a Hypertonic Solution
- Water concentration: Water concentration inside the cell is higher than outside the cell.
- Solute Concentration: Solute concentration inside the cell is lower than outside the cell.
Effect of Hypertonic Solution on Animal Cell

- If an animal cell such as red blood cell is placed into a hypertonic solution, water molecules is transported out from the red blood cells by osmosis (as shown in the diagram above).
- The red blood cells will shrink due to the lost of water from the cell and probably die.
- The red blood cells are said to undergo crenation .
The Youtube video above shows the effects of hypertonic solution on red blood cells. We can see that the cells finally shrink in hypertonic solution.
Effect of Hypertonic Solution on Plant Cell

- When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water molecules is transported out from the cell by osmosis.
- The vacuole and cytoplasm are then shrink due to lost of water.
- The plasma membrane is pulled away from the cell wall..
- The process is called plasmolysed.
Summary:

3.2.2 Types of Solution – Isotonic
What is Isotonic Solution?
In isotonic solutions, both solutions have equal water potential.Water Concentration and Solute Concentration of a Cell in a Isotonic Solution
Water concentration and solute concentration are equal in both solutions.Effect of Isotonic Solution on Animal Cell

- If an animal cell such as red blood cell is placed into a isotonic solution, amount of water molecules is transported into the red blood cells by osmosis is equal to the amount of water molecules transported out from the cell (as shown in the diagram above).
- Therefore the amount of water in the cell remain unchanged.
- The red blood cells maintain their shape.
The Youtube video above shows the effects of isotonic solution on red blood cells. All the cells remain unchanged in isotonic solution.
Effect of Isotonic Solution on Plant Cell

- When a plant cell is placed in an isotonic solution, solute concentration in the external solution is equal to the solute concentration i the cell sap.
- Therefore the rate of diffusion of water into the cell is equal to the rate of diffusion of water out from the cell.
- As a result, the shape of the cell remain unchanged.
3.2.1 Types of Solution – Hypotonic
What is Hypotonic Solution?
Hypotonic solution is the solution that has higher water potential than the other solution.Water Concentration and Solute Concentration of a Cell in a Hypotonic Solution
- Water concentration: Water concentration inside the cell is lower than outside the cell.
- Solute Concentration: Solute concentration inside the cell is higher than outside the cell.
Effect of Hypotonic Solution on Animal Cell

- If an animal cell such as red blood cell is placed into a hypotonic solution, water molecules is transported into the red blood cells by osmosis (as shown in the diagram above).
- The red blood cells will inflate and finally burst because the thin membrane cannot withstand the high pressure inside the cell.
- The red blood cells are said to undergo haemolysis.
The Youtube video above shows the effects of hypotonic solution on red blood cells. We can see that the cells finally burst and become "blur" under the microscope.
Effect of Hypotonic Solution on Plant Cell

- When a plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, water molecules is transported into the cell by osmosis.
- The water is then stored in vacuole causing it to expand and exerts pressure on the cell wall. This pressure is called turgor pressure.
- The turgor pressure caused the plant cell to become firm or turgid.
- The rigid cell wall prevents cell from bursting.